3.2 Playbooks 高级二
when 满足某条件执行
某些场景下我们部署一个软件,或者执行一条命令是有条件的,比如当检测到一条命令的输出中包含 OK 字符串,才进一步执行后续操作
- shell: my_command_here
register: my_command_result
- command: do-something-to-my-app
when: "'ready' in myapp_result.stdout"
亦或是检测到定义了某个变量才执行某些后续操作
#此时 is_db_server 需要是bool值
- yum: name=mysql-server state=present
when: is_db_server
#避免变量未定义报错
- yum: name=mysql-server state=present
when: (is_db_server is defined) and is_db_server
#尝试转换 is_db_server 为bool值
- yum: name=mysql-server state=present
when: is_db_server | bool
参考示例:https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/registered_var/main1.yml
Ansible对playbook的各种解析都发生在控制节点,在控制节点把相关操作做好再发送到被控节点,因此被控节点几乎不需要任何依赖包
loop 循环
类似与批量拷贝多个文件、批量创建多个用户这样的需求,我们可以使用循环来提高效率
# 这里的 item 是固定用法
- name: Add several users
ansible.builtin.user:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
password: "{{ '123456' | password_hash('sha512', 'mysecretsalt') }}"
loop:
- testuser1
- testuser2
数据类型为字典,示例如下
- name: Create files
# ansible.builtin.file:
file:
dest: "{{ item.path }}"
state: touch
mode: "{{ item.mode }}"
loop:
- { path: '/tmp/foo1.txt', mode: '0444' }
- { path: '/tmp/foo2.txt', mode: '0444' }
- { path: '/tmp/foo3.txt', mode: '0444' }
参考示例:https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/playbooks_loops
ignore_errors 忽略错误
默认情况下,如下两种情况被Ansible认为是错误
- 对于shell或者command模块,返回非0即错误,返回0正确(跟shell自带逻辑一致)
- 对于模块返回failure即错误 (模块内置的机制,基本无需关注)
一旦某个指令返回错误,Ansible将停止在该机器继续执行后面的指令,但是其它机器不受影响,如下示例使Ansible忽略错误
# 忽略错误,无论是否有错误,继续往下执行
- name: test2
shell: cat /etc/redhat-release-xxx
ignore_errors: yes
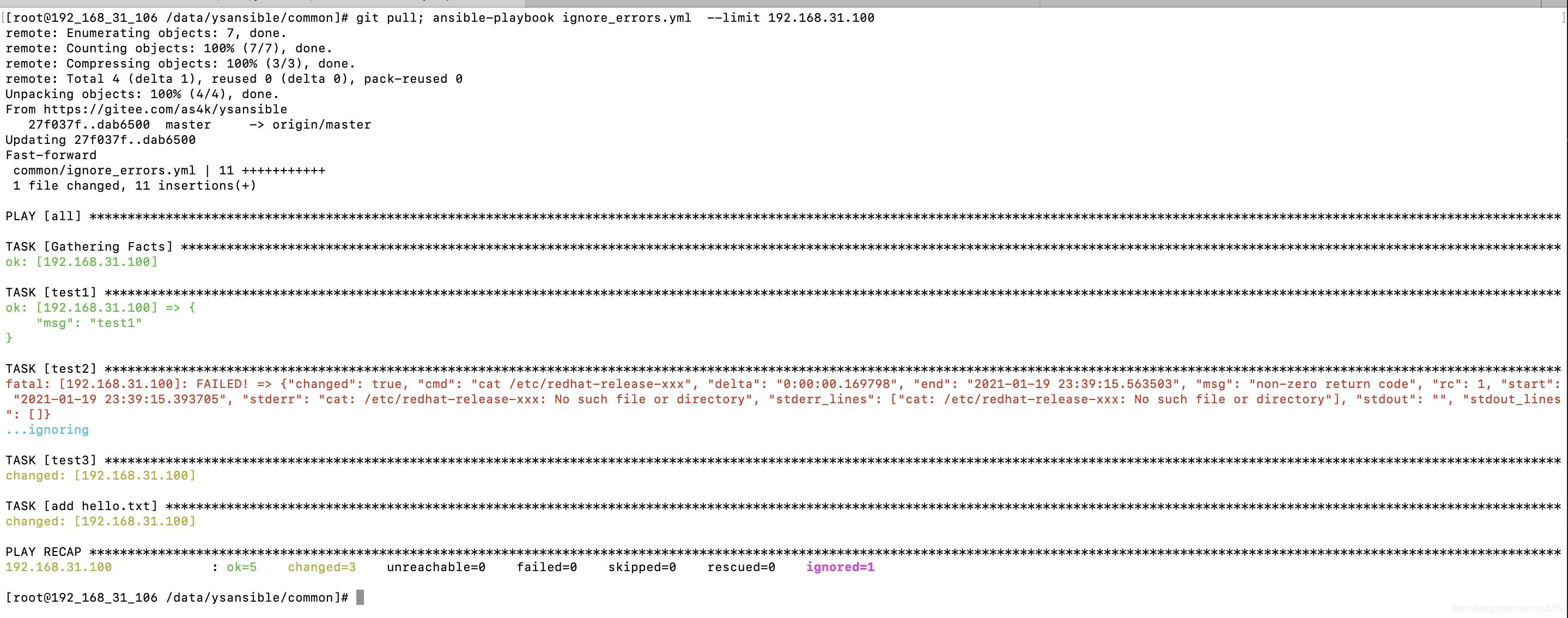
ignore_errors只能忽略指令执行本身的错误,对于类似机器无法连通、YAML文件语法错误,则无法忽略
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/ignore_errors.yml
changed_when 定义什么是改变
如果我们使用的不是Ansible自带的模块,而是shell或者command模块,那么无论指令多么简单,Ansible都会认为目标机器的状态发生了改变
不是所有需要的功能Ansible都有很好的模块支持,事实上在Ansible Playbook中使用大量的shell命令是常有的事,如果每次执行playbook都有一大堆changed状态输出,能不慌吗!因此我们有必要控制一下,或者说告诉Ansible什么情况下才叫状态changed,比如在shell命令中,我们知道返回值如果是0表示正常,非0表示不正常,即可利用这点来书写很多shell脚本,在Ansible中也有类似的用法
# .rc 在这里是固定用法表示 return code
- name: Report 'changed' when the return code is not equal to 0
shell: cat /etc/redhat-release
register: my_result
changed_when: "my_result.rc != 0"
如果条件比较复杂,比如多个条件需要同时满足,则像下面这样书写
- name: Combine multiple conditions to override 'changed' result
command: /bin/fake_command
register: result
changed_when:
- '"ERROR" in result.stderr'
- result.rc == 2
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/changed_when/main1.yml
failed_when 定义什么是错误
changed_when是Ansible不知道什么是改变,我们告诉它,类似的,failed_when是Ansible不知道什么是错误,或者说什么算作错误情况,由我们定义错误的条件,告诉Ansible在这种情况下判断为错误,如下面的示例,我们通过命令的返回值进行字符串匹配来判断命令执行成功与否
- name: test5
shell: cat /tmp/ok.txt
register: my_result
failed_when: "'error' in my_result.stdout"
#my_result.stdout 表示标准输出
#my_result.stderr 表示标准错误
#my_result.rc 表示返回值
如果需要多个条件同时满足,即 并且
failed_when:
- result.rc == 0
- '"No such" not in result.stdout'
如果需要或条件
failed_when: diff_cmd.rc == 0 or diff_cmd.rc >= 2
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/changed_when/main1.yml
delegate_to 任务委派
我们知道Ansible执行指令的时候都是绑定机器的,比如如果我们看到下面这样一行命令
ansible-playbook main1.yml --limit 192.168.31.100
默认情况下,我们都是认为这份playbook上的指令逐一在192.168.31.100机器上进行执行(不考虑类似使用ssh远程执行脚本这种反常操作)
不过有些时候,我们部署一套服务,需要用到多个机器,而且并不是现在机器A执行xxx,然后去B执行xxx,这种顺序的,可能是类似A、B、A这种交叉的顺序,比如我们手动从零开始做一下MySQL数据库的主从,大致的流程可能是
- 搭建主库A
- 搭建从库B
- 去主库A上查看binlog位置
- 在从库上执行change master … 构建主从
如果上述操作对应的Ansible中,也就是一份安装从库的playbook,内部不仅要在从库上执行相关命令,还需要跨机器到主库上执行一些相关命令,类似这种一个任务不是在当前机器执行,而是需要委派到其它机器上执行的操作,就需要用到 delegate_to
如下示例,演示了在指定机器增加一条hosts记录解析
- name: add test domain to another host
lineinfile:
path: /etc/hosts
regexp: '^192.168.31.100'
line: 192.168.31.100 as4k.top
delegate_to: 192.168.31.101
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/delegate_to.yml
wait_for 等待某条件满足
某些服务在启动的时候,需要其它服务已经正常运行才能启动,如很多程序在启动前必须要求数据库能够正常连接,否则会启动失败,wait_for给我们提供诸如等待某个端口连通,等待某个文件存在,然后才继续向下执行Ansible指令
干等10秒再继续执行playbook后面的指令
- name: Sleep for 10 seconds and continue with play
wait_for:
timeout: 10
等待某个端口打开后再继续
- name: 等待5秒,检查目标机器8000端口是否打开,如果持续10秒还没有打开,返回失败
wait_for:
port: 8000
delay: 5
timeout: 10
#超时时间默认为300秒
等待某个文件存在再继续
- name: Wait until the file /tmp/foo is present before continuing
wait_for:
path: /tmp/foo
等待某个文件不存在再继续
- name: Wait until the lock file is removed
wait_for:
path: /var/lock/file.lock
state: absent
等待某个文件里包含某个字符串再继续
- name: Wait until the string "completed" is in the file /tmp/foo before continuing
wait_for:
path: /tmp/foo
search_regex: completed
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/wait_for.yml
当然关于服务之间依赖的管理有很多方法,如每个程序内置依赖检查机制,比如应用程序检查到数据库无法连通,自动重试之类
完全在本地执行playbook
有些时候我们仅仅是测试一些Ansible的基础功能,我们可以本地配置免密,本地执行,不过Ansible有专门的参数,可以让这件事情更快
使用参数 --connection=local
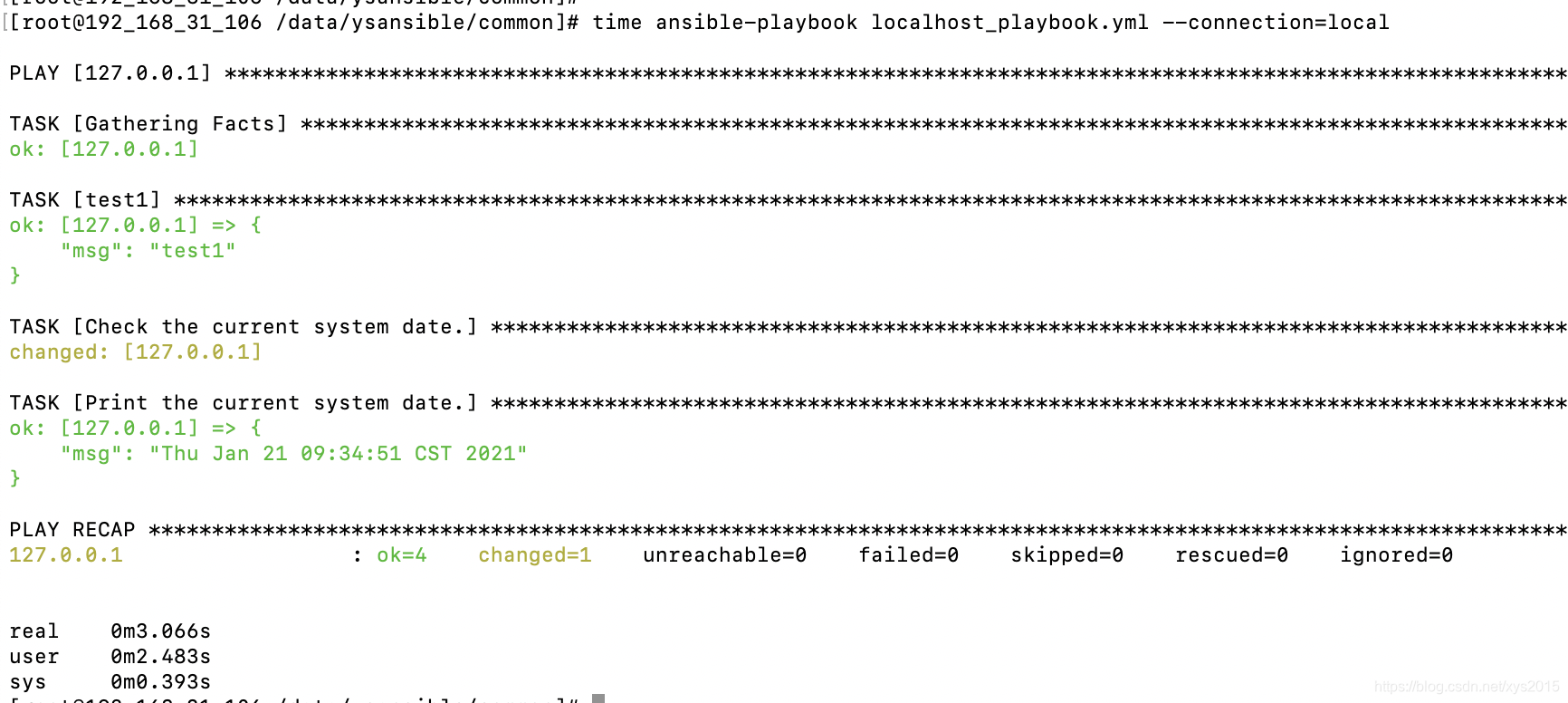 参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/localhost_playbook.yml
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/localhost_playbook.yml
prompt 让用户交互输入信息
同shell脚本类似,Ansible也可以交互等待用户输入信息,存入变量里备用,如等待用户输入账号密码等
vars_prompt:
- name: share_user
prompt: "What is your username?"
private: no
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/prompt.yml
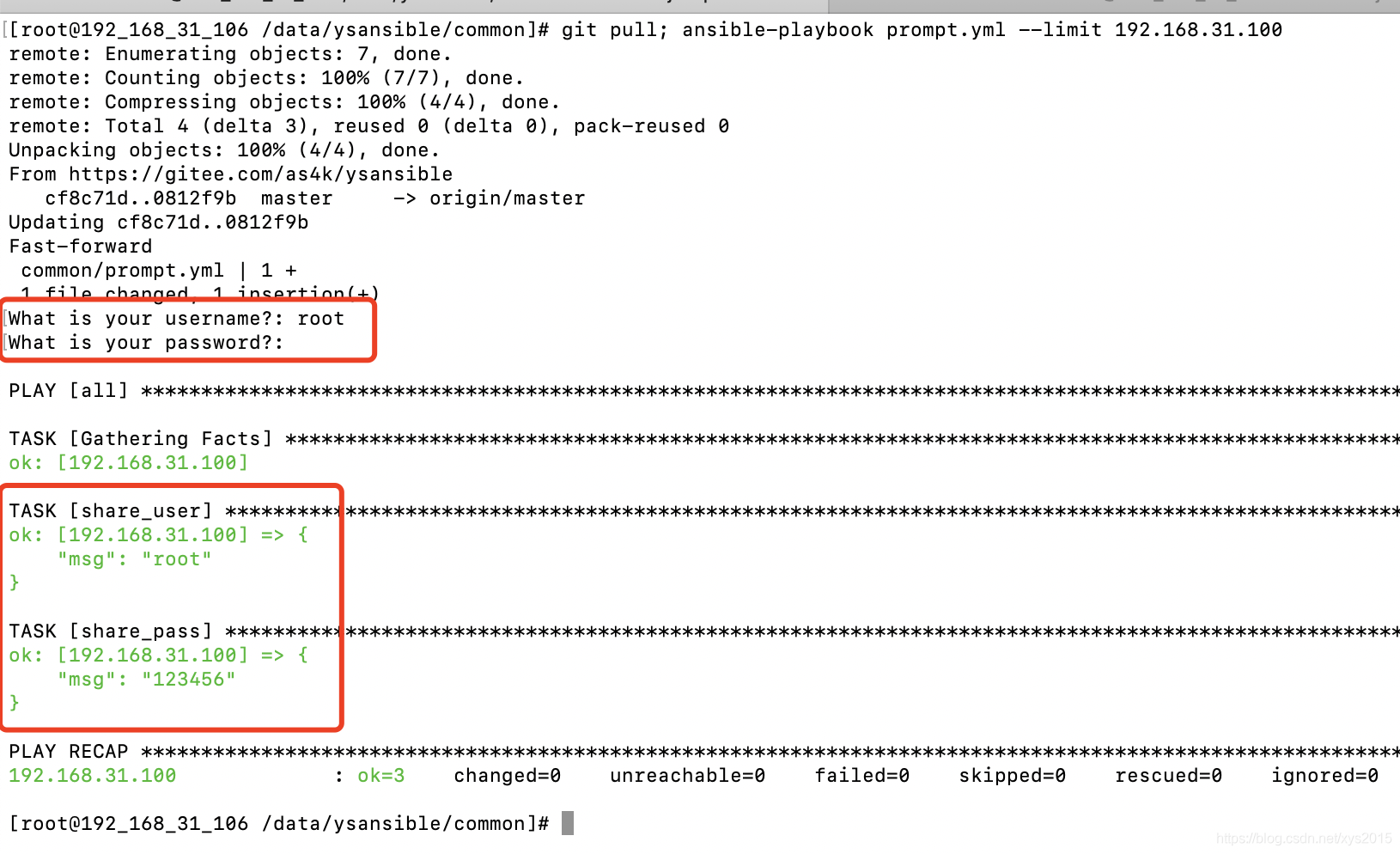
除非必要这种方式最好少用、不用,Ansible本来是自动化配置工具,需要传递的信息建议使用变量的形式直接放到文本里,这种方式也可以变相的实现某种程度上的安全
tags 给任务分类
给playbook里的任务打上标签(tags),这样在执行时,可以指定只运行带有某个标签的,或者带有某个标签的不去运行
- name: hello3 4 5
debug:
msg: "hello3 4 5"
tags:
- hello3
- hello4
不指定tag,则全部执行
ansible-playbook tags.yml --limit 192.168.31.100
指定具体的tag,则只执行该tag下面的任务
ansible-playbook tags.yml --tags hello2 --limit 192.168.31.100
跳过hello2标签(即取反)
ansible-playbook tags.yml --skip-tags hello2 --limit 192.168.31.100
指定多个tag
ansible-playbook tags.yml --tags "hello3,hello4,hello5" --limit 192.168.31.100
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/tags.yml
在使用标签的时候,团队内部最好有相关的规范,做好文档,不要到处滥用标签功能,否则维护起来比较麻烦,试想一下一份playbook里有一堆标签,并且也没有什么文档,那这些标签是啥功能几乎无从得知,只能一行行去阅读分析
block 任务分组
Block是Ansible2.0开始引入的功能,将一堆任务分组,这样方便我们进行组级别的统一控制,例如当满足条件1,执行任务A、B、C,当满足条件2执行任务D、E、F,类似这样的需求,那么利用block把A、B、C划分到一组,而把D、E、F划分到另一组,比较方便
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
#Install and configure Apache on RHEL/CentOS hosts.
- block:
- yum: name=httpd state=present
- template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
when: ansible_os_family == 'RedHat'
become: yes
#Install and configure Apache on Debian/Ubuntu hosts.
- block:
- apt: name=apache2 state=present
- template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
- service: name=apache2 state=started enabled=yes
when: ansible_os_family == 'Debian'
become: yes
利用block还可以实现类似编程语言中的,捕获异常的功能
- block:
- name: look something
shell: cat /etc/redhat-release
# shell: cat /etc/redhat-release-xxx
rescue:
- name: rescue xxx
debug:
msg: "命令执行失败 走这里(执行成功这里被忽略)"
always:
- name: always xxx
debug:
msg: "无论命令是否执行成功 这里都走"
这种方式理解起来还是比较复杂的,不易维护,简单处理失败用上面说的 failed_when 和 changed_when
参考示例 https://gitee.com/as4k/ysansible/blob/master/common/block.yml
参考资料
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_error_handling.html
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/wait_for_module.html
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_loops.html