mysql-基础
概览
MySQL版本选择:
5.6 版本: GA 6-12个月 小版本是偶数版本
5.7 版本: GA 6-12个月 小版本是偶数版本 5.7.17以上版本 (MGR:高可用)
General Availability (GA) Releases
MySQL历史版本下载地址 https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
GA版是软件产品正式发布的版本,也称生产版本的产品。
安装MySQL需要考虑的步骤
1 Determine whether MySQL runs and is supported on your platform.
https://www.mysql.com/support/supportedplatforms/database.html
2 Choose which distribution to install.
3 Download the distribution that you want to install.
4 Install the distribution.
a binary distribution or a source distribution
5 Perform any necessary postinstallation setup.
How to Get MySQL
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mirrors.html
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/repo/yum/
MySQL 二进制 离线安装
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/binary-installation.html
########################## 需要安装的依赖 ##################################################
yum search libaio
yum search libnuma
yum install libaio numactl-libs
########################## 创建用户 ##########################################################
groupadd mysql
useradd -r -g mysql -s /bin/false mysql
后面启动MySQL服务的时候指定这个用户,MySQL数据目录的权限需要授权为mysql用户
########################## 解压文件 ##########################################################
mkdir -p /xdata && cd /xdata
wget http://192.168.1.8/chfs/shared/mysql/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
tar xf mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
官方文件下载地址 https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
########################## 创建和授权数据目录 #############################################
cd /xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64
mkdir -p /xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/data-mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql /xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/data-mysql
########################## 初始化数据目录 ##################################################
初始化的数据目录要保持为空,否则会报错
bin/mysqld --help --verbose &> /tmp/tmp.txt #这条命令可以查看到MySQL配置文件的生效顺序
bin/mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql --basedir=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 --datadir=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/data-mysql
bin/mysql_ssl_rsa_setup --help
bin/mysql_ssl_rsa_setup --datadir=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/data-mysql
########################## 增加配置文件 ##########################################################
cat << 'EOF' > /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
basedir=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64
datadir=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/data-mysql
EOF
########################## 启动MySQL服务 ##############################################################
bin/mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
此时已经成功监听3306端口
ps aux | grep mysql
If the command fails immediately and prints mysqld ended, look for information in the error log (which by default is the host_name.err file in the data directory).
如果需要替换配置文件,可以使用
mysqld_safe --user=mysql --defaults-file=/data/3307/my.cnf &
########################## 修改root用户的密码 #####################################################
./bin/mysql -u root --skip-password -e "ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'root-password'"
./bin/mysql -u root -p'root-password' -e "select user,host from mysql.user"
########################## 检查MySQL运行状态 ######################################################
bin/mysqladmin -u root -p'root-password' version
bin/mysqladmin -u root -p'root-password' ping
bin/mysqladmin -u root -p'root-password' variables
bin/mysqladmin -u root -p'root-password' --help
########################## 启动和停止MySQL ########################################################
bin/mysqladmin -uroot -p'root-password' shutdown
bin/mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
########################## 配置systemd管理MySQL ###########################################################
cat << 'EOF' > /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service
[Unit]
Description=MySQL Community Server
After=network.target
After=syslog.target
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Alias=mysql.service
[Service]
User=mysql
Group=mysql
# Execute pre and post scripts as root
PermissionsStartOnly=true
# Start main service
ExecStart=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/bin/mysqld_safe
# Give up if ping don't get an answer
TimeoutSec=600
Restart=always
PrivateTmp=false
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart mysqld
systemctl status mysqld
systemctl enable mysqld
########################## 添加MySQL环境变量 ###########################################################
echo 'export PATH=/xdata/mysql-5.7.28-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/bin:$PATH' >> /etc/profile
重新连接终端
echo $PATH
mysql -u root -p'root-password' -e "select user,host from mysql.user"
########################## 创建最高权限root用户 ###########################################################
默认安装的root用户只能在本地连接(localhost),如果我们希望其它机器也能连接这个MySQL,需要重新创建个账号
mysql -uroot -p'root-password' -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO root@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'root-password' WITH GRANT OPTION"
mysql -h$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}') -uroot -p'root-password' -e "DROP USER 'root'@'localhost'"
MySQL YUM 在线安装
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/linux-installation-yum-repo.html
http://192.168.31.50/chfs/shared/mysql/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm
[root@node2 ~]# #yum install ./mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm
[root@node2 ~]# rpm -ql mysql80-community-release
/etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-mysql
/etc/yum.repos.d/mysql-community-source.repo
/etc/yum.repos.d/mysql-community.repo
yum install yum-utils
yum repolist all | grep mysql | grep enabled
yum-config-manager --disable mysql80-community
yum-config-manager --enable mysql57-community
[root@node2 ~]# yum repolist all | grep mysql | grep enabled
mysql-connectors-community/x86_64 MySQL Connectors Community enabled: 153
mysql-tools-community/x86_64 MySQL Tools Community enabled: 110
mysql57-community/x86_64 MySQL 5.7 Community Server enabled: 424
yum install mysql-community-server
systemctl start mysqld
shell> sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
shell> mysql -uroot -p
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass4!';
MySQL YUM 离线安装
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/linux-installation-rpm.html
https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
####################################### 解压 rpm tar 包 ##########################################################
mkdir -p /as4k/mysql && cd /as4k/mysql
wget http://192.168.1.8/chfs/shared/mysql/mysql-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar
OR http://as4k.top:7000/chfs/shared/mysql/mysql-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar
tar xf mysql-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm-bundle.tar
####################################### 安装 #####################################################################
这一步的写法非常重要,我是直接把官方文档照搬下来的,不这样通配符形式的写,很可能会报一些依赖错误之类
yum install mysql-community-{server,client,common,libs}-* -y
有可能需要依赖 yum install libaio
####################################### 启动 #####################################################################
systemctl start mysqld.service
systemctl enable mysqld.service
systemctl status mysqld.service
####################################### 创建新的root账号 #####################################################################
MySQL5.7 YUM安装,启动的时候会指定初始化数据目录,并且生成一个随机密码,生成的root用户是面向localhost登录的,下面做的工作是,创建高权限跨机器可登录的root用户,删除旧的root用户,主要默认是开启了密码强度策略的,密码简单则无法创建
grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log | awk '{print $NF}'
XPWD=`grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log | awk '{print $NF}'`; echo $XPWD
mysql --connect-expired-password -uroot -p"$XPWD" -e "ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'As4k.top'"
mysql -uroot -p'As4k.top' -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO root@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'As4k.top' WITH GRANT OPTION"
mysql -h$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}') -uroot -p'As4k.top' -e "DROP USER 'root'@'localhost'"
mysql -uroot -p'As4k.top' -e "select user,host from mysql.user"
MySQL 插件安装或卸载
windows
validate_password 为例
https://blog.csdn.net/kk185800961/article/details/79447754
常用SQL
################################## 未分类 ##################################################################
select * from error_queue_meta limit 10\G;
################################## 查看当前正在运行的SQL ##############################################################
show processlist;
################################## 连接和退出 ########################################################################
mysql --help
shell> mysql -h host -u user -p
shell> mysql -u root -p'As4k.top'
mysql> exit OR quit OR \q
mysql> \s
################################## 未分类 ########################################################################
如果输入的查询命令包含密码等敏感信息,比如下面的命令
mysql> select user,host,password from mysql.user;
使用上下按键翻的时候,是翻不出来,相当于没有记录。但是可以在日志记录里完全可以找到。
因此这个参数不太安全,生产中一般不太常用。该参数是基于session的,只在当前会话中生效,除非
配置在配置文件中。
在mysql命令行中,可以用\G,格式化查询,看起来的效果,就是横转竖向
命令敲错,在MySQL5.6中可以敲\c退出,而在5.7中可以使用CTRL+C直接取消当前命令。
在5.6中CTRL+C直接退出数据库。
################################## 不区分大小写 ########################################################################
MySQL的查询语句,不区分大小写,下面的写法效果一样
mysql> SELECT VERSION(), CURRENT_DATE;
mysql> select version(), current_date;
mysql> SeLeCt vErSiOn(), current_DATE;
################################## 多行输入 ########################################################################
Here is a simple multiple-line statement:
mysql> SELECT
USER(),
CURRENT_DATE;
################################## 取消输入 ########################################################################
取消当前输入 \c
Prompt Meaning
mysql> Ready for new query
-> Waiting for next line of multiple-line query
'> Waiting for next line, waiting for completion of a string that began with a single quote (')
"> Waiting for next line, waiting for completion of a string that began with a double quote (")
`> Waiting for next line, waiting for completion of an identifier that began with a backtick (`)
/*> Waiting for next line, waiting for completion of a comment that began with /*
################################## Creating and Using a Database ###################################################
SHOW DATABASES;
CREATE DATABASE xtest;
USE xtest
SHOW TABLES;
CREATE TABLE pet (name VARCHAR(20), owner VARCHAR(20),
species VARCHAR(20), sex CHAR(1), birth DATE, death DATE);
DESCRIBE pet;
INSERT INTO pet
VALUES ('Puffball','Diane','hamster','f','1999-03-30',NULL);
################################## Retrieving Information from a Table ###############################################
SELECT what_to_select
FROM which_table
WHERE conditions_to_satisfy;
SELECT * FROM pet;
UPDATE pet SET birth = '1989-08-31' WHERE name = 'Bowser';
Selecting Particular Rows
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name = 'Bowser';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE birth >= '1998-1-1';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE species = 'dog' AND sex = 'f';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE species = 'snake' OR species = 'bird';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE (species = 'cat' AND sex = 'm')
OR (species = 'dog' AND sex = 'f');
Selecting Particular Columns
SELECT name, birth FROM pet;
SELECT owner FROM pet;
SELECT DISTINCT owner FROM pet;
SELECT name, species, birth FROM pet
WHERE species = 'dog' OR species = 'cat';
Sorting Rows
SELECT name, birth FROM pet ORDER BY birth;
SELECT name, birth FROM pet ORDER BY birth DESC;
SELECT name, species, birth FROM pet
ORDER BY species, birth DESC;
Date Calculations
SELECT name, birth, CURDATE(),
TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,CURDATE()) AS age
FROM pet;
SELECT name, birth, CURDATE(),
TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,CURDATE()) AS age
FROM pet ORDER BY name;
SELECT name, birth, CURDATE(),
TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,CURDATE()) AS age
FROM pet ORDER BY age;
SELECT name, birth, death,
TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,death) AS age
FROM pet WHERE death IS NOT NULL ORDER BY age;
SELECT name, birth, MONTH(birth) FROM pet;
SELECT name, birth FROM pet WHERE MONTH(birth) = 5;
Working with NULL Values
SELECT 1 IS NULL, 1 IS NOT NULL;
SELECT 1 = NULL, 1 <> NULL, 1 < NULL, 1 > NULL;
SELECT 0 IS NULL, 0 IS NOT NULL, '' IS NULL, '' IS NOT NULL;
Pattern Matching
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name LIKE 'b%';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name LIKE '%fy';
To find names containing a w
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name LIKE '%w%';
To find names containing exactly five characters, use five instances of the _ pattern character:
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name LIKE '_____';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name REGEXP '^b';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name REGEXP BINARY '^b';
SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name REGEXP 'w';
Counting Rows
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM pet;
SELECT owner, COUNT(*) FROM pet GROUP BY owner;
SELECT species, COUNT(*) FROM pet GROUP BY species;
Using More Than one Table
mysql> SELECT pet.name,
TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,date) AS age,
remark
FROM pet INNER JOIN event
ON pet.name = event.name
WHERE event.type = 'litter';
mysql> SELECT p1.name, p1.sex, p2.name, p2.sex, p1.species
FROM pet AS p1 INNER JOIN pet AS p2
ON p1.species = p2.species
AND p1.sex = 'f' AND p1.death IS NULL
AND p2.sex = 'm' AND p2.death IS NULL;
################################## Getting Information About Databases and Tables ##############################
SELECT DATABASE();
SHOW TABLES;
DESCRIBE pet;
################################## 排序 ########################################################################
mysql> select * from pipeline_info where data_as4k=467 ORDER BY pipeline_info_id DESC limit 5;
+------------------+------------------+---------+----------------+-------------------+-------------------------+---------------+-----------------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------+---------------+-------------------------+------------+-------------------------+------------+
| pipeline_info_id | data_as4k | dest_id | dest_schema_id | processed_records | total_processed_records | total_records | last_record_timestamp | last_sync_time | lastday_max_delay | today_max_delay | active_status | created_at | created_by | updated_at | updated_by |
+------------------+------------------+---------+----------------+-------------------+-------------------------+---------------+-----------------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------+---------------+-------------------------+------------+-------------------------+------------+
| 621919866 | 467 | 54 | 12908 | 1 | 28546996 | 28546996 | 2020-05-08 02:25:03 | 2020-05-08 02:26:25 | 234198 | 140345 | 1 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 |
| 621919865 | 467 | 54 | 15726 | 1 | 228 | 228 | 2020-04-03 06:36:59 | 2020-04-03 06:37:37 | NULL | NULL | 1 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 |
| 621919864 | 467 | 54 | 12910 | 44 | 6175 | 6175 | 2020-03-30 06:11:52 | 2020-03-30 06:12:42 | NULL | NULL | 1 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 |
| 621919863 | 467 | 54 | 16958 | 60 | 25360312 | 25360312 | 2020-05-08 02:45:18 | 2020-05-08 02:45:55 | 146173 | 712994 | 1 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 |
| 621919862 | 467 | 54 | 12911 | 1 | 25200 | 25200 | 2020-05-08 02:31:52 | 2020-05-08 02:32:25 | 31238 | 31489 | 1 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 | 2020-05-08 02:48:00.000 | 2 |
+------------------+------------------+---------+----------------+-------------------+-------------------------+---------------+-----------------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------+---------------+-------------------------+------------+-------------------------+------------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
################################## 删除 ########################################################################
MySQL DELETE 语句
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE Clause]
DELETE FROM runoob_tbl WHERE runoob_id=3;
delete,drop,truncate 都有删除表的作用,区别在于:
1、delete 和 truncate 仅仅删除表数据,drop 连表数据和表结构一起删除,打个比方,delete 是单杀,truncate 是团灭,drop 是把电脑摔了。
2、delete 是 DML 语句,操作完以后如果没有不想提交事务还可以回滚,truncate 和 drop 是 DDL 语句,操作完马上生效,不能回滚,打个比方,delete 是发微信说分手,后悔还可以撤回,truncate 和 drop 是直接扇耳光说滚,不能反悔。
3、执行的速度上,drop>truncate>delete,打个比方,drop 是神舟火箭,truncate 是和谐号动车,delete 是自行车。
- SQL语句分类 Chapter 13 SQL Statement Syntax
- 数据结构定义
- 开发规范,数据库名一律使用小写
- 库相关操作
- 创建库
CREATE DATABASE as4k - 查看库
SHOW DATABASES - 查看创建库的语句
SHOW CREATE DATABASE as4k - 查看创建库的帮助
HELP CREATE DATABASE - 删除库
drop database as4k
- 创建库
- 表相关操作
HELP CREATE TABLE- 创建表,哪些字段,数据类型,主键,自增,非空,唯一键,默认值,非负数,注释
SHOW CREATE TABLE student- 查看表
SHOW TABLES - 查看表中字段的定义
DESC student - 删除表
DROP TABLE student - 修改表结构
- 修改表名
ALTER TABLE student RENAME stu - 添加列和列定义
ALTER TABLE stu ADD age INT - 添加多个列
ALTER TABLE stu ADD test VARCHAR(20), ADD qq INT - 添加字段到表的首位
ALTER TABLE stu ADD classid VARCHAR(20) FIRST - 添加新字段到指定字段后
ALTER TABLE stu ADD phone INT AFTER age - 删除指定字段
ALTER TABLE stu DROP qq - 修改字段的属性
ALTER TABLE stu MODIFY sid VARCHAR(20) - 修改字段名及属性
ALTER TABLE stu CHANGE phone telphone CHAR(20)
- 修改表名
- 数据记录操作
- 插入 INSERT
- 插入单条数据
INSERT INTO tbl_name (col1,col2) VALUES(15,col1*2) - ID主键自增,可省略,或使用NULL占位
- 插入多条数据
INSERT INTO tbl_name (a,b,c) VALUES(1,2,3),(4,5,6),(7,8,9)
- 插入单条数据
- 更新 UPDATE
- UPDATE命令还是比较危险的,一般规范的做法都是指定条件更新
- 指定条件更新
UPDATE student SET gender='f' WHERE sid=1 - 全表更新
UPDATE student SET gender='f' WHERE 1=1
- 删除 DELETE
- DELETE删除操作的实现机制是一条条遍历记录来删除,该命令被归为DML
- 删除一个表的全部记录
TRUNCATE TABLE studentORDELETE FROM student - DELETE与TRUNCATE区别可见
help truncate table - 指定条件删除某一条记录
DELETE FROM student WHERE sid=3此操作比较危险,而且不太必要 - 一般我们不希望主键ID变动,比如班级里每个学生都有学号,一个学生走了,后面的学生学号还是不变
- 可以通过额外添加state字段来模拟删除的操作
- 插入 INSERT
- 数据库账号管理
- 新建账号并授权
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO as4k@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' - 新建具有授权权限的账号
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO as4k@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' WITH GRANT OPTION - 具有授权这个权限相当于能够新建用户,但是新建用户的权限不会超过自身的权限
- 收回某些权限
REVOKE SELECT ON *.* FROM root@'localhost' - 查看指定账号具有的权限
SHOW GRANTS FOR as4k@'localhost' - 创建账号
CREATE USER 'jeffrey'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' - 删除账号
DROP USER 'as4k'@'localhost' - 如果某个账号已经登录,则删除该账号不会立刻退出会话,要等到下一次登录才生效
- 重命名某个账号
RENAME USER 'xudao'@'localhost' TO 'zengdao'@'localhost' - 修改账号密码
SET PASSWORD FOR 'as4k'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('123456')
- 新建账号并授权
- 查询相关SQL(SELECT)
- 简单计算
SELECT 1 + 1 - 查看表中全部记录
SELECT * FROM as4k - 查询指定字段
SELECT countrycode,district FROM city - 限制输出条数
SELECT * FROM city LIMIT 2,2(编程语言可以利用此特性做分页) - 条件查询
SELECT name,population FROM city WHERE countrycode='CHN' - 多条件
SELECT name,population FROM city WHERE countrycode='CHN' AND district='heilongjiang' - 模糊查询
SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode LIKE '%H%'(与通配符匹配相似,不区分大小写) - 排序查询
SELECT * FROM city ORDER BY col_name [ASC | DESC] - 范围查询
SELECT * FROM city WHERE population>=1410000
- 简单计算
非交互使用 MySQL
mysql < batch-file
mysql -e "source batch-file"
mysql -h host -u user -p < batch-file
SQL的执行过程
简述SQL的执行过程(连接层——SQL层——存储引擎层)。
- 连接层
- 提供连接协议(TCP/IP、socket)
- 验证用户的合法性
- 接收SQL语句,并传递给SQL层
- SQL层
- 接收连接层传来的SQL语句
- 判断语法(如果语法有错,报语法错误)
- 判断语义
- 解析器
- 优化器
- 执行器
- 提供一个专用线程和存储引擎层交互
- 如果有缓存,记录到缓存,记录日志
存储引擎层
- 接收SQL层传来的SQL语句
- 去文件中取出相应数据
- 结构化成表,返回给SQL层
客户端连接工具通过网络或本地socket连接到服务端(mysqld)
根据用户名,主机名,密码确认用户是否能成功登录
登录成功后,客户端发送SQL请求到服务端
服务端解析客户端请求的SQL语句,若果有语法错误直接报错
服务端验证根据权限表,验证用户是否有权限执行指定的SQL语句
如果要执行的SQL已经存放在缓存里,则直接返回
优化器对查询语句进行必要的优化
存储引擎与磁盘进行交互,将相关数据返回给用户
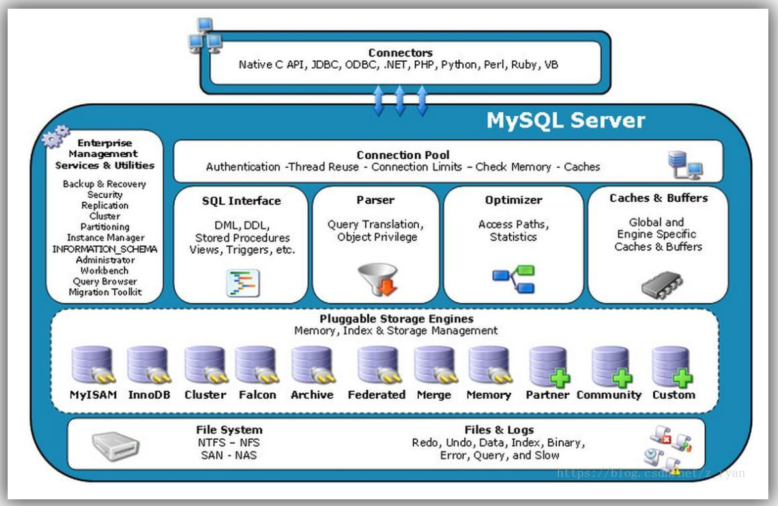
MySQL 课程体系
MySQL Programs
mysqld
The SQL daemon (that is, the MySQL server). To use client programs, mysqld must be running, because clients gain access to databases by connecting to the server.
mysqld_safe
A server startup script. mysqld_safe attempts to start mysqld.
mysql.server
A server startup script. This script is used on systems that use System V-style run directories containing scripts that start system services for particular run levels. It invokes mysqld_safe to start the MySQL server.
mysql_install_db
This program initializes the MySQL data directory, creates the mysql database and initializes its grant tables with default privileges, and sets up the InnoDB system tablespace. It is usually executed only once, when first installing MySQL on a system.
mysql_plugin
This program enables you to improve the security of your MySQL installation.
mysql_ssl_rsa_setup
This program creates the SSL certificate and key files and RSA key-pair files required to support secure connections, if those files are missing. Files created by mysql_ssl_rsa_setup can be used for secure connections using SSL or RSA.
mysql
The command-line tool for interactively entering SQL statements or executing them from a file in batch mode.
mysqladmin
A client that performs administrative operations, such as creating or dropping databases, reloading the grant tables, flushing tables to disk, and reopening log files. mysqladmin can also be used to retrieve version, process, and status information from the server.
MySQL 配置文件
查看正在使用的配置文件路径 mysqld --verbose --help

##################### 一份简单的配置文件示例 ####################################################################
[root@db01 ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
datadir=/data/3307/data
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
socket=/data/3307/mysql.sock
log_error=/data/3307/mysql.err
log-bin=/data/3307/mysql-bin
server_id=1
port=3307
##################### Option Files Read on Unix and Unix-Like Systems ######################################
File Name Purpose
/etc/my.cnf Global options
/etc/mysql/my.cnf Global options
SYSCONFDIR/my.cnf Global options
$MYSQL_HOME/my.cnf Server-specific options (server only)
defaults-extra-file The file specified with --defaults-extra-file, if any
~/.my.cnf User-specific options
~/.mylogin.cnf User-specific login path options (clients only)
加上`--defaults-file`,加上这个参数以上配置文件均不读取。
如果配置冲突,读取顺序靠后的配置文件会覆盖前面的配置文件,也就是"后来者居上",这点与Shell环境变量类似。另外很多选项是可以直接在命令中指定的,命令行中的选项优先于所有配置文件。
##################### Option File Syntax #######################################################################
注释 #comment OR ;comment
##################### Here is a typical global option file: ######################################################
[group]
group is the name of the program or group for which you want to set options. After a group line, any option-setting lines apply to the named group until the end of the option file or another group line is given. Option group names are not case-sensitive.
[client]
port=3306
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
port=3306
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
key_buffer_size=16M
max_allowed_packet=8M
[mysqldump]
quick
##################### Here is a typical user option file: ######################################################
[client]
# The following password will be sent to all standard MySQL clients
password="my password"
[mysql]
no-auto-rehash
connect_timeout=2
##################### Option File Inclusions #######################################################################
!include /home/mydir/myopt.cnf
!includedir /home/mydir
MySQL makes no guarantee about the order in which option files in the directory are read.
Any files to be found and included using the !includedir directive on Unix operating systems must have file names ending in .cnf
##################### 查看某个配置是否生效 ##############################################################################
mysql -p'As4k.top' -e "show variables" | grep "max_allowed_packet"
To determine the default command option and system variable values used by the server, execute this command:
shell> mysqld --verbose --help
To see the current system variable values actually used by the server as it runs, connect to it and execute this statement:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES;
##################### 动态修改配置 ##########################################################################################
Many MySQL programs have internal variables that can be set at runtime using the SET statement.
mysql> SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet=16M;
####################### 下划线和中划线是一样的 #################################################################################
If you like, underscores in a variable name can be specified as dashes. The following option groups are equivalent. Both set the size of the server's key buffer to 512MB:
[mysqld]
key_buffer_size=512M
[mysqld]
key-buffer-size=512M
####################### 未分类 #############################################################################################
Using System Variables
The MySQL server maintains many system variables that configure its operation.
Each system variable has a default value.
System variables can be set at server startup using options on the command line or in an option file. Most of them can be changed dynamically while the server is running by means of the SET statement, which enables you to modify operation of the server without having to stop and restart it.
Many system variables are built in. System variables implemented by a server plugin are exposed when the plugin is installed and have names that begin with the plugin name. For example, the audit_log plugin implements a system variable named audit_log_policy.
There are two scopes in which system variables exist. Global variables affect the overall operation of the server. Session variables affect its operation for individual client connections. A given system variable can have both a global and a session value. Global and session system variables are related as follows:
At runtime, system variable names must be written using underscores, not dashes. The following examples briefly illustrate this syntax:
Set a global system variable:
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 1000;
SET @@GLOBAL.max_connections = 1000;
Set a session system variable:
SET SESSION sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET @@SESSION.sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET @@sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
Some system variables can be enabled with the SET statement by setting them to ON or 1, or disabled by setting them to OFF or 0. However, to set such a variable on the command line or in an option file, you must set it to 1 or 0; setting it to ON or OFF will not work. For example, on the command line, --delay_key_write=1 works but --delay_key_write=ON does not.
##################################################################### Program Option Modifiers #################################
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/option-modifiers.html
下面的3种用法等价:
--disable-column-names
--skip-column-names
--column-names=0
下面的3种用法等价:
--column-names
--enable-column-names
--column-names=1
The values ON, TRUE, OFF, and FALSE are also recognized for boolean options (not case-sensitive).
If an option is prefixed by --loose, a program does not exit with an error if it does not recognize the option, but instead issues only a warning:
shell> mysql --loose-no-such-option
mysql: WARNING: unknown option '--loose-no-such-option'
The --loose prefix can be useful when you run programs from multiple installations of MySQL on the same machine and list options in an option file. An option that may not be recognized by all versions of a program can be given using the --loose prefix (or loose in an option file). Versions of the program that recognize the option process it normally, and versions that do not recognize it issue a warning and ignore it.
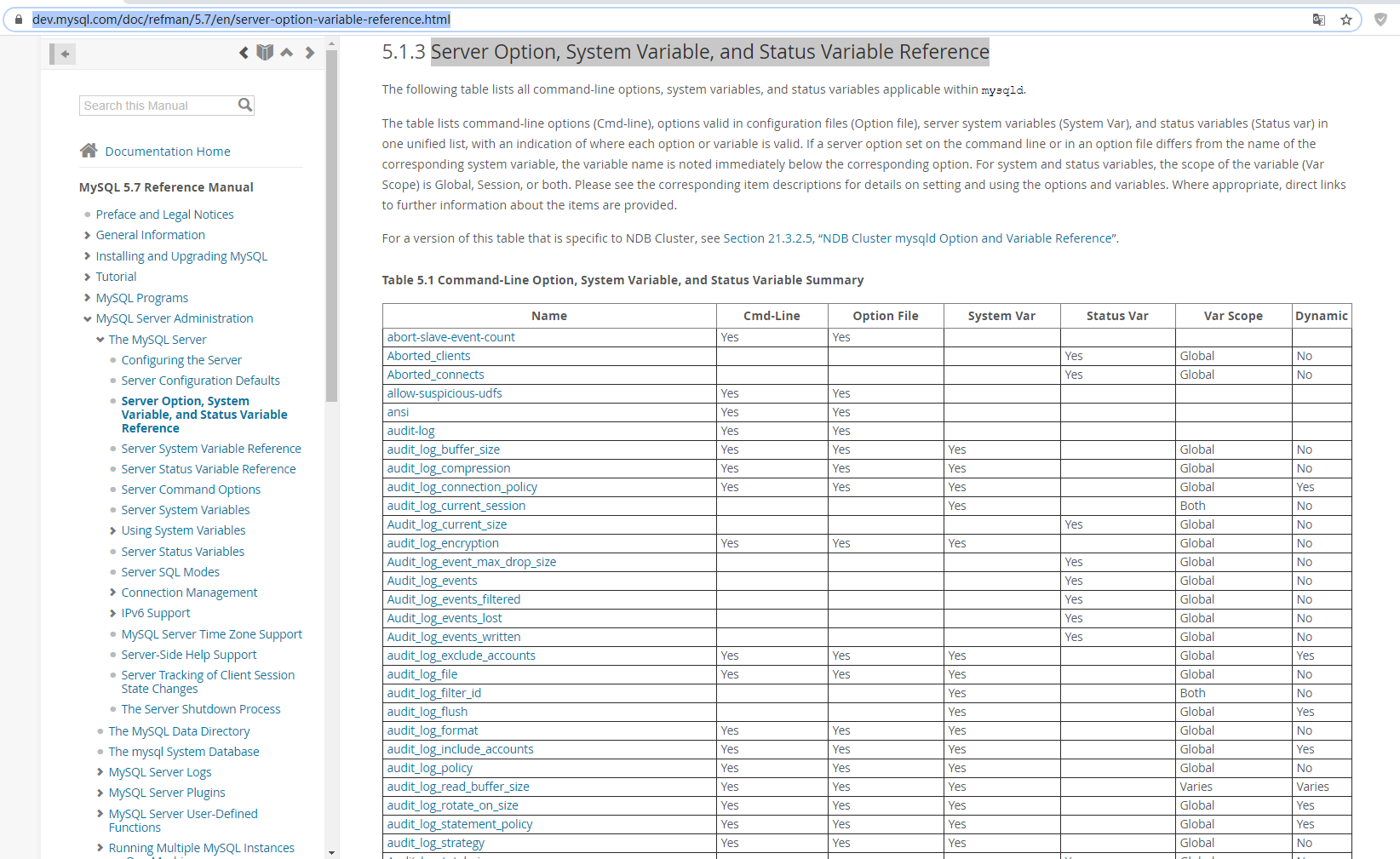
MySQL 全部配置文件参考大全
Server Option, System Variable, and Status Variable Reference
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-option-variable-reference.html
MySQL 日志
MySQL Server has several logs that can help you find out what activity is taking place.
Log Type Information Written to Log
Error log Problems encountered starting, running, or stopping mysqld
General query log Established client connections and statements received from clients
Binary log Statements that change data (also used for replication)
Relay log Data changes received from a replication master server
Slow query log Queries that took more than long_query_time seconds to execute
DDL log (metadata log) Metadata operations performed by DDL statements
By default, no logs are enabled
By default, the server writes files for all enabled logs in the data directory.
You can force the server to close and reopen the log files (or in some cases switch to a new log file) by flushing the logs. Log flushing occurs when you issue a FLUSH LOGS statement;
On Unix and Unix-like systems, mysqld uses the --log-error option to determine whether mysqld writes the error log to the console or a file, and, if to a file, the file name:
If --log-error is not given, mysqld writes the error log to the console.
If --log-error is given without naming a file, mysqld writes the error log to a file named host_name.err in the data directory.
If --log-error is given to name a file, mysqld writes the error log to that file (with an .err suffix added if the name has no suffix), located under the data directory unless an absolute path name is given to specify a different location.
If --log-error is given in an option file in a [mysqld], [server], or [mysqld_safe] section, mysqld_safe finds and uses the option, and passes it to mysqld.
It is common for Yum or APT package installations to configure an error log file location under /var/log with an option like log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log in a server configuration file. Removing the file name from the option causes the host_name.err file in the data directory to be used.
If the server writes the error log to the console, it sets the log_error system variable to stderr. Otherwise, the server writes the error log to a file and sets log_error to the file name.
############################### Error Log File Flushing and Renaming ###############################
mv host_name.err host_name.err-old
mysqladmin flush-logs
mv host_name.err-old backup-directory
MySQL 插件机制
MySQL Server Plugins
MySQL supports a plugin API that enables creation of server components. Plugins can be loaded at server startup, or loaded and unloaded at runtime without restarting the server.
############################### Installing and Uninstalling Plugins ###############################
Plugins installed with the INSTALL PLUGIN statement:
[mysqld]
plugin-load=myplugin=somepluglib.so
INSTALL PLUGIN myplugin SONAME 'somepluglib.so';
The plugin library file base name depends on your platform. Common suffixes are .so for Unix and Unix-like systems, .dll for Windows.
INSTALL PLUGIN also causes “permanent” plugin registration: The plugin is listed in the mysql.plugin table to ensure that the server loads it on subsequent restarts.
Many plugins can be loaded either at server startup or at runtime. However, if a plugin is designed such that it must be loaded and initialized during server startup, attempts to load it at runtime using INSTALL PLUGIN produce an error
To uninstall a plugin that currently is loaded at server startup with a plugin-loading option, use this procedure.
Remove any options related to the plugin from the my.cnf file.
Restart the server.
Plugins normally are installed using either a plugin-loading option at startup or with INSTALL PLUGIN at runtime, but not both. However, removing options for a plugin from the my.cnf file may not be sufficient to uninstall it if at some point INSTALL PLUGIN has also been used. If the plugin still appears in the output from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS or SHOW PLUGINS, use UNINSTALL PLUGIN to remove it from the mysql.plugin table. Then restart the server again.
############################### Obtaining Server Plugin Information ###############################
While a plugin is loaded, information about it is available from the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS table and the SHOW PLUGINS statement.
There are several ways to determine which plugins are installed in the server:
The INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS table contains a row for each loaded plugin. Any that have a PLUGIN_LIBRARY value of NULL are built in and cannot be unloaded.
mysql> SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS\G
The SHOW PLUGINS statement displays a row for each loaded plugin. Any that have a Library value of NULL are built in and cannot be unloaded.
mysql> SHOW PLUGINS;
+----------------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------+---------+
| Name | Status | Type | Library | License |
+----------------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------+---------+
| binlog | ACTIVE | STORAGE ENGINE | NULL | GPL |
| mysql_native_password | ACTIVE | AUTHENTICATION | NULL | GPL |
| sha256_password | ACTIVE | AUTHENTICATION | NULL | GPL |
| CSV | ACTIVE | STORAGE ENGINE | NULL | GPL |
.....
| FEDERATED | DISABLED | STORAGE ENGINE | NULL | GPL |
| partition | ACTIVE | STORAGE ENGINE | NULL | GPL |
| ngram | ACTIVE | FTPARSER | NULL | GPL |
| validate_password | ACTIVE | VALIDATE PASSWORD | validate_password.so | GPL |
+----------------------------+----------+--------------------+----------------------+---------+
45 rows in set (0.00 sec)
The mysql.plugin table shows which plugins have been registered with INSTALL PLUGIN. The table contains only plugin names and library file names, so it does not provide as much information as the PLUGINS table or the SHOW PLUGINS statement.
############################### Controlling Plugin Activation State ###############################
If the server knows about a plugin when it starts (for example, because the plugin is named using a --plugin-load option or is registered in the mysql.plugin table), the server loads and enables the plugin by default. It is possible to control activation state for such a plugin using a --plugin_name[=activation_state] startup option, where plugin_name is the name of the plugin to affect, such as innodb, csv, or validate_password. As with other options, dashes and underscores are interchangeable in option names. Also, activation state values are not case-sensitive. For example, --my_plugin=ON and --my-plugin=on are equivalent.
--plugin_name=OFF
Tells the server to disable the plugin. This may not be possible for certain built-in plugins, such as mysql_native_password.
--plugin_name[=ON]
Tells the server to enable the plugin. (Specifying the option as --plugin_name without a value has the same effect.) If the plugin fails to initialize, the server runs with the plugin disabled.
Plugin activation states are visible in the LOAD_OPTION column of the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PLUGINS table.
Suppose that CSV, BLACKHOLE, and ARCHIVE are built-in pluggable storage engines and that you want the server to load them at startup, subject to these conditions: The server is permitted to run if CSV initialization fails, must require that BLACKHOLE initialization succeeds, and should disable ARCHIVE. To accomplish that, use these lines in an option file:
[mysqld]
csv=ON
blackhole=FORCE
archive=OFF
The --enable-plugin_name option format is a synonym for --plugin_name=ON. The --disable-plugin_name and --skip-plugin_name option formats are synonyms for --plugin_name=OFF.
############################### 未分类 ################################################################################
A password-validation plugin implements password strength policies and assesses the strength of potential passwords.
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/validate-password.html
Group Replication enables you to create a highly available distributed MySQL service across a group of MySQL server instances, with data consistency, conflict detection and resolution, and group membership services all built-in.
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/group-replication.html
MySQL 用户管理
CREATE USER 'xudao'@'127.0.0.1';
CREATE USER 'xudao_ugly'@'127.0.0.1' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
SELECT USER,HOST FROM mysql.user;
SHOW GRANTS FOR xudao_ugly@127.0.0.1;
'用户名'@'主机域'
10.0.0.%
10.0.%.%
10.0.0.0/255.255.255.0
######################## 使用grant直接创建用户 ######################################################
GRANT SELECT,UPDATE,DROP,DELETE ON *.* TO xudao_old@127.0.0.1 IDENTIFIED BY '123';
######################## 删除用户 ##############################################################
drop user xudao@'127.0.0.1';
######################## 修改用户密码 ############################################################
grant update alter set mysqladmin 这五种方式都可以修改用户密码。
注意要修改密码,需要当前用户具有更改其它用户密码的权限才行。
**1** GRANT ALL ON *.* TO xudao_old@127.0.0.1 IDENTIFIED BY '1234';
**2** UPDATE mysql.user SET PASSWORD=PASSWORD('5678') WHERE USER='xudao_old' AND HOST='127.0.0.1';
**3** alter 暂时不讲
**4** SET PASSWORD=PASSWORD('5678'); 更改当前登录用户的密码
**5** mysqladmin -h127.0.0.1 -uxudao_old -p5678 PASSWORD '123'; 在SHELL中直接修改。只能更改本地localhost主机用户的密码,不可用更改远端连接用户的密码,127.0.0.1主机也不可以更改。
########################################## 忘记root密码后如何恢复 ##########################################
1 先跳过授权表,启动MySQL --skip-grant-tables (安装起见,跳过网络) --skip-networking
2 登录MySQL,直接登录敲回车,无需输入密码
3 使用upate命令修改密码
4 刷新授权表 flush privileges;
mysql> update mysql.user set password=PASSWORD('root') where user='root' and host='localhost';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
########################################## 用户权限 ###########################################################
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO as4k@'10.0.0.%' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
权限 作用对象 归属 密码
ALL PRIVILEGES 与 ALL 功能是一样的。相当于简写。
单库 单表 所有库所有表 授权可以精确到字段。
grant select(host) on mysql.user to xudao_5@'localhost' identified by '123';
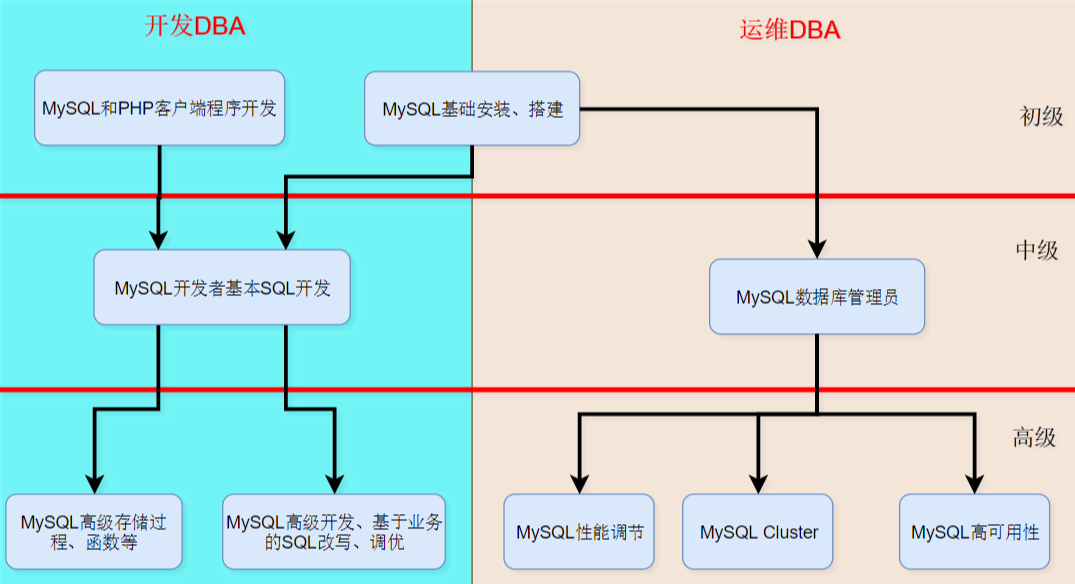
运维DBA与开发DBA
重置ROOT密码
官方手册B.5.3.2 How to Reset the Root Password对root密码忘记如何重置,有详细介绍。
方法1
1 关闭mysqld服务
shell> pkill mysql
shell> netstat -lntup | grep mysql
2 创建初始化密码配置文件
shell> cat /tmp/mysql-init
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('123456');
shell> chown mysql:mysql /tmp/mysql-init
3 用上面的配置文件启动mysqld服务
shell> mysqld --user=mysql --init-file=/tmp/mysql-init &
4 此时root用户密码已被修改为123456,可重启mysqld进行测试。
方法2
假设我们不是简单的忘记,’root’@‘localhost’ 的密码,而且直接手残删除了root账号,也就是SELECT user,host from mysql.user已经看不见root账号。假设当前会话还没退出,则我们直接重新创建root账号并授权即可,可是我们又二次手残已经退出当前会话,即使这样我们还可以通过下面的方式恢复root账号。
1 重新启动mysqld,跳过授权表,跳过网络
shell> pkill mysql
shell> mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
跳过授权表则客户端登录MySQL Server无需密码,跳过网络则不允许任何远程客户端登录本机MySQL Server,这是出于安全方面的考虑,一旦跳过网络会发现本机根本没有3306端口。
2 直接登录MySQL Server,刷新权限表
shell> mysql
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
如果不刷新授权表,则GRANT等授权命令无法使用。先关闭再刷新开启,由于我们已经处于当前登录会话,不会自动退出。
3 重新创建root用户,权限打满
mysql> CREATE USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'root'@'localhost';
mysql> SELECT * FROM mysql.user\G
4 重新正常启动mysqld,使用新密码(123456)连接
shell> pkill mysql
shell> /etc/init.d/mysqld start
shell> mysql -uroot -p123456
mysql> \s
整体思路
正常root密码忘记,root账号还在,建议使用方法1即可,方法2也可以直接使用INSERT的方法,往表中插入一行root账号的信息。
MySQL主机名的多种书写方式
SQL pattern matching enables you to use _ to match any single character and % to match an arbitrary
number of characters (including zero characters).
% 匹配任意多个字符(包括零个)
_ 匹配任意单个字母
1) username@'主机域'
2)主机域:可以理解为是MySQL登陆的白名单
3)主机域格式:
10.0.0.51
'10.0.0.5%'
'10.0.0.%'
'10.0.%.%'
'10.%.%.%'
'%'
'db01'
'10.0.0.51/255.255.255.0'
恢复InnoDB表结构
- 先把world.sql下载导入3308实例中
- 删除3309的data目录(或者 拷贝world目录到3309/data下)
- 拷贝3308的data目录到3309下
- 修复world库中的所有表的独立表空间
0 多实例的启动和关闭
关闭
pkill mysql
启动
mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/data/3307/my.cnf &
mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/data/3308/my.cnf &
mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/data/3309/my.cnf &
mysql -S /data/3308/mysql.sock -e "show variables like 'server_id'"
1 进入3307示例,导入world.sql数据库
shell> mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/data/3307/my.cnf &
shell> mysql -S /data/3307/mysql.sock
mysql> source /root/world.sql
mysql> select * from world.city limit 10;
+----+----------------+-------------+---------------+------------+
| ID | Name | CountryCode | District | Population |
+----+----------------+-------------+---------------+------------+
| 1 | Kabul | AFG | Kabol | 1780000 |
| 2 | Qandahar | AFG | Qandahar | 237500 |
| 3 | Herat | AFG | Herat | 186800 |
| 4 | Mazar-e-Sharif | AFG | Balkh | 127800 |
| 5 | Amsterdam | NLD | Noord-Holland | 731200 |
| 6 | Rotterdam | NLD | Zuid-Holland | 593321 |
| 7 | Haag | NLD | Zuid-Holland | 440900 |
| 8 | Utrecht | NLD | Utrecht | 234323 |
| 9 | Eindhoven | NLD | Noord-Brabant | 201843 |
| 10 | Tilburg | NLD | Noord-Brabant | 193238 |
+----+----------------+-------------+---------------+------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2 把3307实例world数据文件复制到3308实例
shell> mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/data/3308/my.cnf &
shell> cp -a /data/3307/data/world /data/3308/data
shell> mysql -S /data/3308/mysql.sock
此时登录到3308实例上,可以看到world库里的表,但是不能使用,会报找不到表错误,如下:
mysql> select * from world.city limit 10;
ERROR 1146 (42S02): Table 'world.city' doesn't exist
3 以city表为例,在3308实例上创建新表new_city
新表的表结构和原表是一样的,这套建表语句在真实环境中我们需要找开发要,现在模拟环境,我们可以登录到3307实例,使用show create table city来得到
由于外键的特殊限制,我们需要把建表语句中的外键删除。
mysql> show create table world.city\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: city
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `city` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` char(35) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`CountryCode` char(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`District` char(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`Population` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`),
KEY `CountryCode` (`CountryCode`),
CONSTRAINT `city_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`CountryCode`) REFERENCES `country` (`Code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4080 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
修改上述语句如下:
USE world;
CREATE TABLE `new_city` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Name` char(35) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`CountryCode` char(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`District` char(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`Population` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`),
KEY `CountryCode` (`CountryCode`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4080 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
4 删除3308实例,new_city的表空间
shell> ALTER TABLE new_city DISCARD TABLESPACE;
实质就是将物理文件new_city.ibd删除之。
5 将底层的物理文件city.ibd拷贝成new_city.ibd
shell> cd /data/3308/data/world/
shell> ls -lh
total 1012K
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 8.6K Nov 30 20:28 city.frm
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 576K Nov 30 20:28 city.ibd
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 9.0K Nov 30 20:28 country.frm
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 160K Nov 30 20:28 country.ibd
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 8.5K Nov 30 20:28 countrylanguage.frm
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 224K Nov 30 20:28 countrylanguage.ibd
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 65 Nov 30 20:28 db.opt
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 8.6K Nov 30 20:44 new_city.frm
shell> cp -a city.ibd new_city.ibd
Note: *.ibd是数据和索引文件,*.frm表的结构定义文件
至此表数据已经还原完毕,即new_city.ibd和city.ibd数据是一样的。如果此时我们去查询new_city表的内容,会提示表空间已丢失,也就是表结构和表空间关联不上,需要我们重建表结构。
mysql> select * from new_city;
ERROR 1814 (HY000): Tablespace has been discarded for table 'new_city'
下面就是重建表结构。
6 连接3308实例,导入新的表空间
mysql> ALTER TABLE new_city IMPORT TABLESPACE;
7 在3308实例上验证是否可以查询数据
mysql> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM new_city;
+----------+
| COUNT(*) |
+----------+
| 4079 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
8 删除原有表,物理上的表结构和表空间
shell> cd /data/3308/data/world
shell> rm -f city.frm city.ibd
9 在3308实例上修改新表名为旧表
mysql> ALTER TABLE new_city RENAME city;
至此,修复表结构操作完毕。
字符集 连表查询 索引
- 字符集(Character Set)与校对规则(Collation)
- 字符集就是字符编码规则,最常用的规则是utf8
- \s 可以看到4种字符集,服务端,客户端,连接字符集,库字符集
- MySQL的字符集可以定义到库,表,字段
show charset可以看到全部字符集- 校对规则:在当前编码下,字符之间的比较顺序
- cs大小写敏感,ci大小写不敏感,bin二进制编码比较
show collation可以看到全部的校对规则- 最常用的是 utf8_general_ci (ci case insensitive)
- 字符集官方定义 A character set is a set of symbols and encodings.
- 校对规则官方定义 A collation is a set of rules for comparing characters in a character set.
- 客户端在与服务端通信字符集设定
SET NAMES 'utf8' - 字符集与校对规则的设定
- 建库
CREATE DATABASE mydb CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci - 建表
CREATE TABLE test (id int(4)) CHARSET utf8 - 查看帮助
mysql -e 'help create table' | grep charset - CHARSET 是 CHARACTER SET 的别名,可互换
- 字符集和校对规则具有继承的关系,小继承大,表继承库
- 在配置文件中指定字符集,[mysqld]区块,character-set-server=utf8,collation-server=utf8_general_ci
- 建库
- 生产环境更改数据库字符集(做好备份再改)
ALTER DATABASE as4k CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci - 批量修改一大堆表的字符集 备份非数据库到SQL文件,用SED或VIM文本替换,最后导回去
- 连表高级查询(SELECT)
- 根据需求把多张表拼接成一张表,再根据条件,查询。
- 两张无任何关联的表,无法进行多表查询。
- 所谓表与表之间有关联,一般是指某个字段数据是一致的。
- 比如学生成绩表和学生课程表,这两张表中学生的数据(如学号)是一致的,可以进行连表查询。
- 示例
select t1.sname,t2.mark from t1,t2 where t1.sid=t2.sid and t1.sname='zhang3' - 传统连接 只能内连接,只能取交集
SELECT city.name,city.countrycode,country.name FROM city,country WHERE city.countrycode=country.code AND city.population<100
- 自然连接 (NATURAL JOIN) 自连接的表要有共同的列名字
SELECT city.name,city.countrycode,countrylanguage.language,city.population FROM city NATURAL JOIN countrylanguage WHERE population > 1000000 ORDER BY population;
- 内连接 (企业中多表连接查询) 使用join语句时,小表在前,大表在后。
SELECT city.name,city.countrycode,country.name FROM city JOIN country ON city.countrycode=country.code WHERE city.population<100
- 左外连接
SELECT city.name,city.countrycode,country.name FROM city LEFT JOIN country ON city.countrycode=country.code AND city.population<100
- 右外连接
SELECT city.name,city.countrycode,country.name FROM city RIGHT JOIN country ON city.countrycode=country.code AND city.population<100
- 合并查询
- union 去重复合并, union all 不去重复
SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode='CHN' UNION ALL SELECT * FROM city WHERE countrycode='USA' LIMIT 10
- 索引
- 4种索引类型,BTREE,B+TREE,FULLTEXT,RTREE
- 索引是建立在表的字段上的
- 建立索引是需要消耗资源的,建立完毕后,维护索引同样需要消耗资源,并且复杂度有所提高
- 不是所有的字段都需要建立索引,一般给最常用的查询字段建立索引
- 主键索引(一张表只能有一张主键,PRIMARY KEY = UNIQUE + NOT NULL)
- 添加
ALTER TABLE t2 MODIFY id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY - 删除
ALTER TABLE t2 DROP PRIMARY KEY
- 添加
- 唯一性索引(该字段不允许有重复的数据)
- 添加
ALTER TABLE t2 ADD UNIQUE KEY uni_age(age) - 删除
ALTER TABLE t2 DROP KEY uni_age
- 添加
- 普通索引
- 添加
ALTER TABLE test ADD INDEX index_name(NAME) - 创建
CREATE INDEX index_name ON test(NAME) - 删除
ALTER TABLE test DROP KEY index_name
- 添加
- 查看索引
DESC tb2 - 查看索引详细
SHOW INDEX FROM tb_name - 前缀索引 (一个字段里的数据太长,不需要为整个字段建立索引,则可以考虑建立前缀索引)
ALTER TABLE test ADD INDEX idx_name(NAME(10))
- 联合索引 (多个字段联合,建立一个索引)
- 把最常用来做为条件查询的列放在最前面
- 创建people表
CREATE TABLE people (id INT,NAME VARCHAR(20),age TINYINT,money INT ,gender ENUM('m','f')) - 创建联合索引
ALTER TABLE people ADD INDEX idx_gam(gender,age,money) - 查询时,同样需要按照建立索引的顺序查找,否则只能部分走索引或不走索引
- 在MySQL中使用简单的函数
- 查看表中数据行数
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM city - 查看去重数据行数
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT NAME) FROM city
- 查看表中数据行数
执行计划 索引建立规范
- B+TREE与BTREE的区别
- 在叶子节点添加了相邻节点的指针
- 优化了范围查询
- 执行计划(Query Execution Plan)
- explain命令用来查看语句的执行计划,可以看到有没有走索引,以及走的是什么级别
- 示例
EXPLAIN SELECT NAME,countrycode FROM city WHERE id=1 EXPLAIN | DESCRIBE | DESC是互为别名的关系- 查询数据的两种方式: 全表扫描与索引扫描
- 全表扫描意味着,MySQL不得不从上到下,从左至右扫描整张表,以查询某个数据,因此性能最差,应经量规避
- explain语句显示结果中type为ALL表示为全表扫描
- 什么时候会出现全表扫描?
- 业务确实要获取所有数据
- 不走索引导致的全表扫描
- 没索引
- 索引创建有问题
- 语句有问题
- 常见索引扫描类型
- 最左到右(->),性能从最差到最好,能够达到range级别,我们认为就算走索引了
- index range ref eq_ref const system null
- range:索引范围扫描,对索引的扫描开始于某一点,返回匹配值域的行。显而易见的索引范围扫描是带有between或者where子句里带有<,>查询。
- ref:使用非唯一索引扫描或者唯一索引的前缀扫描,返回匹配某个单独值的记录行。
- eq_ref:类似ref,区别就在使用的索引是唯一索引,对于每个索引键值,表中只有一条记录匹配,简单来说,就是多表连接中使用primary key或者 unique key作为关联条件A
- const、system:当MySQL对查询某部分进行优化,并转换为一个常量时,使用这些类型访问。
- 如将主键置于where列表中,MySQL就能将该查询转换为一个常量
- NULL:MySQL在优化过程中分解语句,执行时甚至不用访问表或索引
- Extra(扩展)
- Using temporary
- Using filesort 使用了默认的文件排序(如果使用了索引,会避免这类排序)
- Using join buffer
- 如果出现Using filesort请检查order by, group by, distinct, join 条件列上有没有索引
- 当order by语句中出现Using filesort,那就尽量让排序值在where条件中出现
- explain key_len 越小越好
- 前缀索引去控制 rows: 越小越好
- 建立索引的规则(规范) SQL语句优化及索引建立规范
- 1 选择唯一性索引
- 唯一性索引的值是唯一的,可以更快速的通过该索引来确定某条记录。
- 注意:如果重复值较多,可以考虑采用联合索引
- 主键索引和唯一键索引,在查询中使用是效率最高的。
- 2 经常需要排序、分组和联合操作的字段建立索引
- 尽量保证用户查询数据最多的列放在联合索引的最前面。
- 需要排序的列,建立联合索引。
- 重复值较多的列,建立联合索引。
- 3 建立前缀索引
- 在列过长的情况下(大列),创建前缀索引。创建索引时,排序速度快。
- 之前,在大列上创建索引,未使用前缀索引,导致创建索引2小时。
- 例如:TEXT和BLOG类型的字段,进行全文检索会很浪费时间。如果只检索字段前面的若干个字符,这样可以提高检索速度。
- 4 限制索引的数目
- 每个索引都需要占用磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。
- 修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦,需要重新排序。
- 5 删除不常用的索引和损坏的索引
ALTER TABLE city DROP INDEX idx_pop- 索引损坏原因:建立索引的列,经常大量修改,可能会导致索引损坏。
- 定期去检查损坏的索引,以及根据用户使用情况找到不常用索引。
- 6 结合limit优化查询结果集大的SQL语句
- 查询结果集是原表中的大部分数据,25%以上,就是全表扫描。
- 若果业务允许,可以使用limit控制。
- 结合业务判断,有没有更好的方式。
- 如果没有更好的改写方案就经量不要在mysql存放这个数据了,放到redis缓存里面。
- 7 隐式转换导致索引失效。这一点应当引起重视,也是开发经常会犯的错误。
- 开发在创建表age数据类型是varchar
- 在查询的时候,where age=‘38’ 按照字符串查询会走索引。
- 在查询的时候,where age=38 按照整数查询,则是全表扫描。
- 8 在生产环境中,把or和in的SQL语句尽量替换成union all
- 避免使用not in和<>,规避全表扫描
- in和or是range级别
- union是ref级别
- 1 选择唯一性索引
表空间-存储引擎-事物
- 什么是MySQL存储引擎
- 可以理解为,MySQL的”文件系统”,只不过功能更加强大。
- 常用的存储引擎有两种: MyISAM 和 InnoDB
- MySQL5.5版本之后,默认的存储引擎是InnoDB
- 存储引擎功能
- 除了可以提供基本的存取功能,还有更多功能事务功能、锁定、备份和恢复、优化以及特殊功能。
- 总之,存储引擎的各项特性就是为了保障数据库的安全和性能设计结构。
- 查看当前MySQL支持的存储引擎类型
SHOW ENGINESORSELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ENGINES
- 查看InnoDB的表有哪些
SELECT table_schema,table_name,engine FROM information_schema.tables WHERE ENGINE='innodb'
- 查看MyISAM的表有哪些
SELECT table_schema,table_name,engine FROM information_schema.tables WHERE ENGINE='myisam'
- InnoDB和MyISAM数据文件
- db.opt 数据库的结构定义和设置
- *.frm 数据表的结构定义
- *.MYD MyISAM表数据文件
- *.MYI MyISAM表索引文件
- ibdata* InnoDB表空间数据文件
- ib_logfile* InooDB日志数据
- *.ibd InnoDB数据和索引
- InnoDB存储引擎的优点
- 事务安全(遵从 ACID)
- MVCC(Multi-Versioning Concurrency Control,多版本并发控制)
- InnoDB 行级别锁定
- Oracle 样式一致非锁定读取
- 表数据进行整理来优化基于主键的查询
- 支持外键引用完整性约束
- 大型数据卷上的最大性能
- 将对表的查询与不同存储引擎混合
- 出现故障后快速自动恢复
- 用于在内存中缓存数据和索引的缓冲区池
- InnoDB核心特性 ★★★
- MVCC
- 事物
- 行级锁
- 热备份
- Crash Safe Recovery(自动故障恢复)
- 查看存储引擎
- 查询默认存储引擎
SELECT @@default_storage_engine - 查看表的存储引擎
- SHOW CREATE TABLE tb_name\G
USE db_name; SHOW TABLE STATUS LIKE 'tb_name'\G
- 查询默认存储引擎
- 存储引擎设置
- 在启动配置文件中设置服务器存储引擎
- default-storage-engine=
- default-storage-engine=
- 使用SET命令为当前客户机会话设置
SET @@storage_engine=<Storage Engine>
- 在 CREATE TABLE 语句指定
CREATE TABLE tb1 (col1 INT) ENGINE = <Storage Engine>
- 在启动配置文件中设置服务器存储引擎
- 共享表空间与独立表空间(InnoDB存储引擎)
- 共享表空间
- 查看共享表空间
./data/ibdata1SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%path%'
- MySQL5.6表空间存放的东西
- 系统数据,undo,临时表
- 5.7版本中默认会将undo和临时表独立出来,5.6版本也可以独立,只不过需要在初始化的时候进行配置
- 配置共享表空间
- 在mysqld区块下增加
innodb_data_file_path=ibdata1:50M;ibdata2:50M:autoextend autoextend必须应用在最后一个表空间上
- 在mysqld区块下增加
- 查看共享表空间
- 独立表空间
- 对于用户自主创建的表,会采用此种模式,每个表由一个独立的表空间进行管理
- 查看独立表空间
./data/db_name/tb_name.ibd - 是否开启
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%per_table%'
- 共享表空间
- InnoDB核心特性-事物(transaction)
- 什么是事物
- 主要针对DML语句(update,delete,insert)
- 一组数据操作执行步骤,这些步骤被视为一个工作单元
- 用于对多个语句进行分组
- 可以在多个客户机并发访问同一个表中的数据时使用
- 所有步骤都成功或都失败
- 如果所有步骤正常,则执行
- 如果步骤出现错误或不完整,则取消全部操作,回退到起点
- 事务ACID特性
- Atomic(原子性)所有语句作为一个单元全部成功执行或全部取消。
- Consistent(一致性)如果数据库在事务开始时处于一致状态,则在执行该事务期间将保留一致状态。
- Isolated(隔离性)事务之间不相互影响。
- Durable(持久性)事务成功完成后,做的所有更改都会准确地记录在数据库中,更改不会丢失。
- 事务的控制语句
- START TRANSACTION(或 BEGIN):显式开始一个新事务
- SAVEPOINT:分配事务过程中的一个位置,以供将来引用
- COMMIT:永久记录当前事务所做的更改
- ROLLBACK:取消当前事务所做的更改
- ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT:取消在 savepoint 之后执行的更改
- RELEASE SAVEPOINT:删除 savepoint 标识符
- SET AUTOCOMMIT:为当前连接禁用或启用默认 autocommit 模式
- 一个成功事务的生命周期
begin; SQL1;SQL2; ... SQLN; commit;
- 一个失败事务的生命周期
begin; SQL1;SQL2; ... SQLN; rollback;
- 事务的自动提交特性
- 现在版本在开启事务时,不需要手工begin,只要你输入的是DML语句,就会自动开启事务。
- 查看自动提交是否开启
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'autocommit'
- 临时关闭
SET autocommit=0 - 永久关闭 在mysqld区块下增加
autocommit=0
- 事务隐式提交情况
- 在事务运行期间,手工执行begin的时候会自动提交上个事务
- 在事务运行期间,加入DDL、DCL操作会自动提交上个事务
- 在事务运行期间,执行锁定语句(lock tables、unlock tables)
- load data infile
- select for update
- 在autocommit=1的时候
- 什么是事物
日志-事件-锁-灾难恢复
- 如何利用事务日志进行灾难恢复
- MySQL靠预写式日志(Write-Ahead Logging)来保证持久性
- 数据文件是先写入日志再写入磁盘数据文件的
- 简单地说,灾难恢复过程可以分为redo(重做)和undo(回退)两个步骤
- redo (重做日志)
- redo,顾名思义”重做日志”,是事务日志的一种
- redo,记录的是,内存数据页的变化过程
- redo工作过程
- update t1 set num=2 where num=1
- 首先将t1表中num=1的行所在数据页加载到内存中buffer page
- MySQL实例在内存中将num=1的数据页改成num=2
- num=1变成num=2的变化过程会记录到,redo内存区域,也就是redo buffer page中
- 当敲下commit命令的瞬间,MySQL会将redo buffer page写入磁盘区域redo log
- 当写入成功之后,commit返回ok,打上一个commit标签
- undo (回滚日志)
- undo,顾名思义”回滚日志”,是事务日志的一种。
- undo工作过程
- 将修改的数据行做一个快照
- 实时写入到undo log中
- 断电重启,检查commit标签
- 有commit标签,数据回滚,没标签则回滚数据
- redo和undo的存放位置
- redo存放在数据目录下的
ib_logfile0 ib_logfile1 ... - undo在5.6版本是存放在共享表空间里,也就是数据目录
ibdata1 - 在MySQL5.7版本,undo日志默认是独立出来的
- redo存放在数据目录下的
- 事物中的锁
- “锁”顾名思义就是锁定的意思。
- 锁的作用: 在事务ACID特性过程中,”锁”和”隔离级别”配合来实现”isolation”隔离性的作用
- 排他锁: 保证在多事务操作时,数据的一致性
- 共享锁: 保证在多事务工作期间,数据查询时不会被阻塞
- 多版本并发控制(MVCC)
- 只阻塞修改类操作,不阻塞查询类操作
- 乐观锁(谁先commit以谁为准)
- 悲观锁(谁先begin以谁为准)
- 锁的粒度
- MyISAM: 低并发锁,表级锁
- InnoDB: 高并发锁,行级锁 (似乎需要主键配合实现)
- 不同的用户可以锁定同一张表的不同行的数据
- 事物的4种隔离级别
- READ UNCOMMITTED (允许事务查看其他事务所进行的未提交更改)
- 其它可以实时看到修改
- READ COMMITTED (允许事务查看其他事务所进行的已提交更改)
- 其它人提交后,则可以看到更改
- REPEATABLE READ (确保每个事务的SELECT输出一致,InnoDB的默认级别,最常用)
- 不退出当前会话,则看不到其它人的修改
- SERIALIZABLE (将一个事务的结果与其他事务完全隔离)
- READ UNCOMMITTED (允许事务查看其他事务所进行的未提交更改)
- MySQL日志
- 错误日志
- 错误日志文件包含了mysqld启动或停止时,以及服务器在运行过程中发生任何严重错误时的相关信息
- 配置
--log-error[=file_name] - 默认存放在数据目录的
hostname.err - 程序内查看
show variables like 'log_error'
- 通用日志(常规日志)
- 记录mysqld内部发生了什么,如果怀疑mysqld运行不太正常,则可开启通用日志,观察更详细的信息
- 默认是关闭的,开启方式,
--log[=file_name] - 临时开启
SET GLOBAL general_log ON - 通用日志记录的东西非常多,通常不建议开启
- 二进制日志 ★★★
- 作用
- 这可以说是MySQL中最重要的日志
- 记录已提交的DML事务语句,并拆分为多个事件(event)来进行记录
- 记录所有DDL、DCL等语句
- 但它不包含没有修改任何数据的语句
- 总之,二进制日志会记录所有对数据库发生修改的操作
- 开启
log-bin=mysql-bin - 默认存放在,数据目录里,如
mysql-bin.000001 mysql-bin.000002 ... - 命令行查看
show binary logsshow master status
- 二进制日志模式
- 语句级(statement-based)
- 配置
binlog_format=statement - 日志记录里包含了原始执行的SQL语句(这会让DBA的维护更方便)
- 缺点是不够健壮,语句级的日志如果应用了MySQL的一些额外特性,比如存储过程、触发器,则可能会导致复制异常
- 配置
- 行级(row-based)
- 配置
binlog_format=row - 记录的信息时一些经过base-64编码的信息,需要使用mysqlbinlog命令查看
- 配置
- 混合模式
- 语句级(statement-based)
- 作用
- 事件
- 在binlog中最小的记录单元为event
- 一个事务会被拆分成多个事件(event)
- 事件特性
- 每个event都有一个开始位置(start position)和结束位置(stop position)
- 所谓的位置就是event对整个二进制的文件的相对位置
- 对于一个二进制日志中,前120个position是文件格式信息预留空间
- MySQL第一个记录的事件,都是从120开始的
- 查看binlog事件
show binlog events in 'mysql-bin.000013'
- 查看行级日志文件
mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -vvv mysql-bin.000013 - 临时关闭binlog
set sql_log_bin=0 - 如果基于binlog全量恢复,成本很高
- 可以用备份恢复+短时间内二进制日志,恢复到故障之前
- 延时从库 如果同一时间内和故障库无关的数据库都有操作,在截取binlog时都会被截取到
- mysqlbinlog -d 参数接库名
- 刷新binlog
flush logs- 重启数据库
- 二进制日志达到上限(max_binlog_size)
- 删除二进制日志
- 原则
- 在存储能力范围内,能多保留则多保留
- 基于上一次全备前的可以选择删除
- 删除方式
- 7天后日志过期
SET GLOBAL expire_logs_days = 7 - 使用purge命令删除
PURGE BINARY LOGS BEFORE now() - INTERVAL 3 day - 根据文件名删除
PURGE BINARY LOGS TO 'mysql-bin.000010' - 全部删除
reset master
- 7天后日志过期
- 原则
- 慢查询日志
- 简单来说就是查询时间比较慢的语句(具体时间可以自己配置)
- 作用
- 是将mysql服务器中影响数据库性能的相关SQL语句记录到日志文件
- 通过对这些特殊的SQL语句分析,改进以达到提高数据库性能的目的
- 默认位置: 数据目录的
hostname-slow.log - 开启方式(默认是关闭状态)
- 开启
slow_query_log = 1 - 指定存放位置
slow_query_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/slow.log - 设定慢查询的阀值(默认10s)
long_query_time=0.05 - 记录没使用索引的查询语句
log_queries_not_using_indexes
- 开启
- 查看慢查询日志 mysqldumpslow
mysqldumpslow -s sort_type -t N log_filemysqldumpslow -s c -t 10 /usr/local/mysql/data/slow.log- -s c表时按照数量排序,-t 10表示显示前10条数据
- 第三方插件查看
yum install percona-toolkit-3.0.11-1.el6.x86_64.rpmpt-query-digest /usr/local/mysql/data/slow.log- 慢查询日志也可以做成WEB界面,图形化展示
- Anemometer基于pt-query-digest将MySQL慢查询可视化
- 错误日志
MySQL的备份和恢复
- 备份的原因
- 备份就是为了恢复
- 尽量减少数据的丢失(公司的损失)
- 备份的类型
- 冷备份
- 这些备份在用户不能访问数据时进行,因此无法读取或修改数据。这些脱机备份会阻止执行任何使用数据的活动。这些类型的备份不会干扰正常运行的系统的性能。但是,对于某些应用程序,会无法接受必须在一段较长的时间里锁定或完全阻止用户访问数据。
- 温备份
- 这些备份在读取数据时进行,但在多数情况下,在进行备份时不能修改数据本身。这种中途备份类型的优点是不必完全锁定最终用户。但是,其不足之处在于无法在进行备份时修改数据集,这可能使这种类型的备份不适用于某些应用程序。在备份过程中无法修改数据可能产生性能问题。
- 热备份
- 这种备份一般只有InnoDB存储引擎支持
- 这些动态备份在读取或修改数据的过程中进行,很少中断或者不中断传输或处理数据的功能。使用热备份时,系统仍可供读取和修改数据的操作访问。
- 冷备份
- 备份的方式
- 逻辑备份 (基于SQL语句的备份)
- binlog
- into outfile
- mysqldump
- replication
- 物理备份 (基于磁盘上数据文件的备份)
- Xtrabackup(percona公司)
- 逻辑备份 (基于SQL语句的备份)
- 备份策略
- 全量备份 full
- 增量备份 increamental
- 备份工具
- mysqldump (逻辑)
- mysql原生自带的很好用的逻辑备份工具
- mysqlbinlog(逻辑)
- 实现binlog备份的原生态命令
- xtrabackup(物理)
- precona公司开发的性能很高的物理备份工具
- mysqldump (逻辑)
- 备份工具使用
- mysqldump
- 它与mysql一样是一款客户端连接MySQL Server的工具
- 连接服务端参数(基本参数):-u 用户, -p 密码, -h 主机域, -P 端口, -S socket文件
- mysqldump [OPTIONS] database [tables]
- mysqldump [OPTIONS] –databases [OPTIONS] DB1 [DB2 DB3…]
- mysqldump [OPTIONS] –all-databases [OPTIONS]
-A, --all-databases全库备份mysqldump -uroot -ppwd -A > /backup/full.sql
--flush-logs, -F在备份时自动刷新binlog(不怎么常用)--master-data=2备份时加入change master语句,0没有,1不注释,2注释-R, --routines备份存储过程和函数数据--triggers备份触发器数据]-x锁表备份(MyISAM温备份)--single-transaction快照备份- gzip压缩备份
mysqldump -uroot -ppwd -A -R --triggers --master-data=2 –single-transaction | gzip > /backup/full.sql.gz
- mysqldump的恢复
- 注意
- mysqldump在备份和恢复时都需要MySQL实例启动为前提
- 一般数据量级100G以内,大约15-30分钟可以恢复(PB、EB就需要考虑别的方式)
- mysqldump是以覆盖的形式恢复数据的
- Xtrabackup (物理备份)
- 对于非innodb表(比如myisam)是直接锁表cp数据文件,属于一种温备。
- 对于innodb的表(支持事务),不锁表,cp数据页最终以数据文件方式保存下来,并且把redo和undo一并备走,属于热备方式。
- 备份时读取配置文件/etc/my.cnf
- 全量备份
innobackupex --user=root --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock --no-timestamp /backup/full
- mysqldump