Linux基础命令
ls
# whatis ls
ls (1) - list directory contents
# ls --help
Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
ls --help
man ls
info ls
ls -a 隐藏文件(以小数点开头的)也显示
ls -l 显示详细信息
ls -l --full-time 详细显示时间
ls -lrht
ls -lrht --full-time
ls --fu
ls -ld /etc 显示/etc目录本身的信息(检查某个目录是否存在)
ls /data/as4k/log/sourcedp/04d1c535335e.log 检查下这个文件存在不
ls -lrhS 按照文件大小排序
场景:当前目录里有一堆日志文件,比如每小时切分一次,每次重新服务都会生成新的日志文件,比如很多容器服务,我们想按照时间排序,最新的日志文件在最下面,可以用ls -lrht
# ls -lrht --full-time
... ...
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 939K 2020-01-20 17:59:55.434263316 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-17
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 940K 2020-01-20 18:59:58.616772252 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-18
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 939K 2020-01-20 19:59:56.557747730 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-19
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 940K 2020-01-20 20:59:59.458317786 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-20
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 939K 2020-01-20 21:59:57.225130138 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-21
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 939K 2020-01-20 22:59:57.454956220 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-22
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 940K 2020-01-20 23:59:57.966655832 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-20-23
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 939K 2020-01-21 00:59:57.455206964 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-00
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 940K 2020-01-21 01:59:58.516803639 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-01
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1020K 2020-01-21 02:59:58.647381418 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-02
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.1M 2020-01-21 03:59:58.692713333 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-03
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.2M 2020-01-21 04:59:58.736699966 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-04
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.1M 2020-01-21 05:59:58.779843969 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-05
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.2M 2020-01-21 06:59:59.770465702 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-06
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.3M 2020-01-21 07:59:59.656080180 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log.2020-01-21-07
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.3M 2020-01-21 08:50:48.336933477 +0000 b44e16dc927f.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 786K 2020-01-21 08:59:59.747588768 +0000 04d1c535335e.log.2020-01-21-08
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 139K 2020-01-21 09:15:07.558135049 +0000 04d1c535335e_hadoop.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.9M 2020-01-21 09:15:07.717134212 +0000 04d1c535335e.log
场景:检查某个目录是否存在
[root@node1 ~]# ls -ld /etc
drwxr-xr-x. 86 root root 8192 Jan 21 14:14 /etc
场景:按文件大小排序查看文件,最大的在最下面
[root@node1 ~]# ls -lrhS
total 58M
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7 Feb 1 09:35 hello2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 14 Feb 1 09:51 hello3.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 46 Jan 31 23:37 md5test.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 93 Jan 31 12:21 test.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.5K Feb 1 09:53 hello1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.1K Dec 13 19:56 WordCount.java
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.4K Jan 20 11:29 tmp.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4.4K Feb 1 15:04 dp.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 58M Jul 18 2019 sdf.tgz
注意:ls不加参数显示在屏幕上横向的,但其实是竖向的
[root@node1 tmp]# ls hello*
hello2.txt hello3.txt hello6.txt hello.txt
[root@node1 tmp]# ls hello* | wc -l
4
[root@node1 tmp]# ls hello* | cat
hello2.txt
hello3.txt
hello6.txt
hello.txt
cd
help cd
cd 来到用户的家园目录
cd - 返回上一次的目录
cd .. 返回上一层目录
cd ../../ 返回上两层层目录
ls /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
pwd
# whatis pwd
pwd (1) - print name of current/working director
man pwd
info pwd
场景:无论脚本在什么位置被执行,路径总是正确
#filename: test.sh
workdir="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" && pwd )"
echo $workdir
#BASH_SOURCE 取得当前执行的shell文件所在的路径及文件名
cp
# whatis cp
cp (1) - copy files and directories
# cp --help
Usage: cp [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DEST
or: cp [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORY
or: cp [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...
Copy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.
cp --help
man cp
info cp
把文件拷贝到目录里,如果这个目录已经存在同名文件,默认是会被覆盖的,并且无任何提示,这有一定的危险性,因此很多linux发行版,给这个命令加上了别名
# which cp
alias cp='cp -i'
/usr/bin/cp
# alias | grep cp
alias cp='cp -i'
这样我们复制文件时,如果出现重名,就会有交互输入 y or n 的提示
如果我们不想让别名生效,可使用命令的绝对路径 /usr/bin/cp ,或者使用撬棍 \cp
-v, --verbose 显示复制的详细信息
-a, --archive 保留原始文件的属性等信息,一般复制目录到别处会用到
-r, --recursive 递归复制,复制目录的时候可以用到
场景:原地复制(备份)
cp install.log install.log.bak
cp install.log{,.bak}
场景:目录在前文件在后
cp -t hello/ install.log as4k.txt
场景:包含某些过滤条件的复制
ls /var/log/ | grep mess
for i in `ls /var/log/ | grep mess`; do echo $i; done
for i in `ls /var/log/ | grep mess`; do cp -a /var/log/$i /root; done;
mkdir
# whatis mkdir
mkdir (1) - make directories
# mkdir --help
Usage: mkdir [OPTION]... DIRECTORY...
Create the DIRECTORY(ies), if they do not already exist.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-m, --mode=MODE set file mode (as in chmod), not a=rwx - umask
-p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed
-v, --verbose print a message for each created directory
--help display this help and exit
场景:创建某个需要的目录
mkdir -p /data/mydir
一般都会加上-p参数,这样目录存在不会报错,自动创建父目录,也就是无需关系是否存在该目录,该目录里是否有数据等
rm
# whatis rm
rm (1) - remove files or directories
# rm --help
Usage: rm [OPTION]... FILE...
-f, --force ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt
-i prompt before every removal
-r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively
-d, --dir remove empty directories
-v, --verbose explain what is being done
--help display this help and exit
By default, rm does not remove directories. Use the --recursive (-r or -R)
option to remove each listed directory, too, along with all of its contents.
To remove a file whose name starts with a '-', for example '-foo',
use one of these commands:
rm -- -foo
rm ./-foo
cp --help
man cp
info cp
删除文件属于高危操作,默认是直接删除,并且无任何提示,这有一定的危险性,因此很多linux发行版,给这个命令加上了别名
# which rm
alias rm='rm -i'
/usr/bin/rm
# alias | grep rm
alias rm='rm -i'
这样我们删除文件时,就会有交互输入 y or n 的提示
如果我们不想让别名生效,可使用命令的绝对路径 /usr/bin/rm ,或者使用撬棍 \cp
常见使用场景
删除目录及目录下的所有子目录和文件
rm -rf dir
若果我们知道要删除的肯定全部都是文件,可不加-r参数,可避免误删除目录
rm -f file*
rm -vf file*
如果我们知道要删除的目录肯定是一个空目录可以使用-d参数
rm -d dir
mv
# whatis mv
mv (1) - move (rename) files
[root@node1 ~]# alias | grep mv
alias mv='mv -i'
[root@node1 ~]# which mv
alias mv='mv -i'
/usr/bin/mv
注意很多系统自带有别名,禁止别名生效可使用 /usr/bin/mv 或 \mv
[root@node1 ~]# mv --help
Usage: mv [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DEST
or: mv [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORY
or: mv [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...
Rename SOURCE to DEST, or move SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.
-f, --force do not prompt before overwriting
-i, --interactive prompt before overwrite
-n, --no-clobber do not overwrite an existing file
-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY move all SOURCE arguments into DIRECTORY
-T, --no-target-directory treat DEST as a normal file
-v, --verbose explain what is being done
--help display this help and exit
mv --help
man mv
info mv
场景:重命名文件
[root@node1 ~]# ls hello1.txt
hello1.txt
[root@node1 ~]# mv -v hello1.txt hello6.txt
‘hello1.txt’ -> ‘hello6.txt’
场景:移动一批文件
[root@node1 ~]# mv -v hello* /tmp
‘hello2.txt’ -> ‘/tmp/hello2.txt’
‘hello3.txt’ -> ‘/tmp/hello3.txt’
‘hello6.txt’ -> ‘/tmp/hello6.txt’
touch
创建文件 touch file.txt
echo
info echo
man echo
'-n'
Do not output the trailing newline. 不打印回车
'-e'
Enable interpretation of the following backslash-escaped characters
in each STRING:
'\n' newline
[root@node1 ~]# echo hello
hello
[root@node1 ~]# echo hello > hello.txt
[root@node1 ~]# cat hello.txt
hello
[root@node1 ~]# echo -n ss
ss[root@node1 ~]#
[root@node1 ~]# echo "sdf\naaa"
sdf\naaa
[root@node1 ~]# echo -e "sdf\naaa"
sdf
aaa
tree
# whatis tree
tree (1) - list contents of directories in a tree-like format.
tree --help
man tree
info tree
-a 显示隐藏文件
-N 显示中文
-dL 1 只显示一级目录
[root@node1 ~]# tree /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
├── ifcfg-eth0
├── ifcfg-eth0.bak
├── ifcfg-lo
├── ifdown -> ../../../usr/sbin/ifdown
├── ifdown-bnep
├── ifdown-eth
├── ifdown-ippp
├── ifdown-ipv6
├── ifdown-isdn -> ifdown-ippp
├── ifdown-post
├── ifdown-ppp
├── ifdown-routes
├── ifdown-sit
├── ifdown-Team
├── ifdown-TeamPort
├── ifdown-tunnel
├── ifup -> ../../../usr/sbin/ifup
├── ifup-aliases
├── ifup-bnep
├── ifup-eth
├── ifup-ippp
├── ifup-ipv6
├── ifup-isdn -> ifup-ippp
├── ifup-plip
├── ifup-plusb
├── ifup-post
├── ifup-ppp
├── ifup-routes
├── ifup-sit
├── ifup-Team
├── ifup-TeamPort
├── ifup-tunnel
├── ifup-wireless
├── init.ipv6-global
├── network-functions
└── network-functions-ipv6
0 directories, 36 files
[root@node1 ~]# rpm -qf /usr/bin/tree
tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64
file
# whatis file
file (1) - determine file type
file --help
man file
[root@node1 ~]# file /usr/bin/cp
/usr/bin/cp: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=d5e29bd19107fc7c0a75cffa392da6ac299add6d, stripped
[root@node1 ~]# file -s /dev/sda
/dev/sda: x86 boot sector; partition 1: ID=0x83, active, starthead 32, startsector 2048, 2097152 sectors; partition 2: ID=0x8e, starthead 170, startsector 2099200, 534771712 sectors, code offset 0x63
[root@node1 ~]# file /dev/sda
/dev/sda: block special
md5sum
linux
# whatis md5sum
md5sum (1) - compute and check MD5 message digest
md5sum --help
# md5sum /etc/passwd
c0245125df18d87d71d2e7968487571c /etc/passwd
[root@node1 ~]# md5sum /etc/passwd | md5sum -c
/etc/passwd: OK
[root@node1 ~]# md5sum /etc/passwd > md5test.txt
[root@node1 ~]# md5sum -c md5test.txt
/etc/passwd: OK
一般如果要传输的文件非常大,或者比较重要,为求稳妥可以做一个md5校验,确保文件传输正确
mac SHA1
➜ Downloads shasum shala-applinzi-com-code-and-data.tar.gz
522413c69b149922849278d3404cd0537b538f2d shala-applinzi-com-code-and-data.tar.gz
windows下校验 SHA1
D:\as4k\xbackup\linux_iso>certutil -hashfile CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1804.iso
SHA1 的 CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1804.iso 哈希:
3a7cb1f2041fee7c3c99c2afc7f1bf60ac671c73
CertUtil: -hashfile 命令成功完成。
official 3a7cb1f2041fee7c3c99c2afc7f1bf60ac671c73 CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1804.iso
local 3a7cb1f2041fee7c3c99c2afc7f1bf60ac671c73 CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1804.iso
cat
# whatis cat
cat (1) - concatenate files and print on the standard output
cat这个命令按照翻译来说,是连接文本的含义
[root@node1 ~]# echo "hello1" > hello1.txt
[root@node1 ~]# echo "hello2" > hello2.txt
[root@node1 ~]# cat hello1.txt hello2.txt
hello1
hello2
[root@node1 ~]# cat hello1.txt hello2.txt > hello3.txt
[root@node1 ~]# cat hello3.txt
hello1
hello2
不过我们一般都是直接用来查看单个文本内容
# cat --help
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output.
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-n, --number number all output lines
--help display this help and exit
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
[root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cat -An
1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash$
2 bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin$
3 daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin$
4 adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin$
5 lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin$
[root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/passwd | cat -An > hello1.txt
[root@node1 ~]# cat -An hello1.txt
1 1^Iroot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash$$
2 2^Ibin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin$$
3 3^Idaemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin$$
4 4^Iadm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin$$
场景:我们需要快速生成一些文本,比如某些简单的配置文件,这些配置文件中有时可能需要用到变量
cat << 'EOF' > /etc/locale.conf
export LANG="en_US.UTF-8"
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"
EOF
cat << 'EOF' >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
source /etc/locale.conf
systemctl restart chronyd.service
EOF
myip=`hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'`
cat << EOF >> /tmp/hello.txt
MASTER_IP=$myip
EOF
less
当文本文件比较大的时候,比如几百页,几M大小的时候,使用cat在同一个屏幕下查看显然就不方便了,此时可以使用less命令进行分页查看
less file 分页查看
less -N file 显示行号
less --help
space(f,PageDown) 下一页
b(PageUp) 上一页
q 退出
G 最后一页
gg 第一页
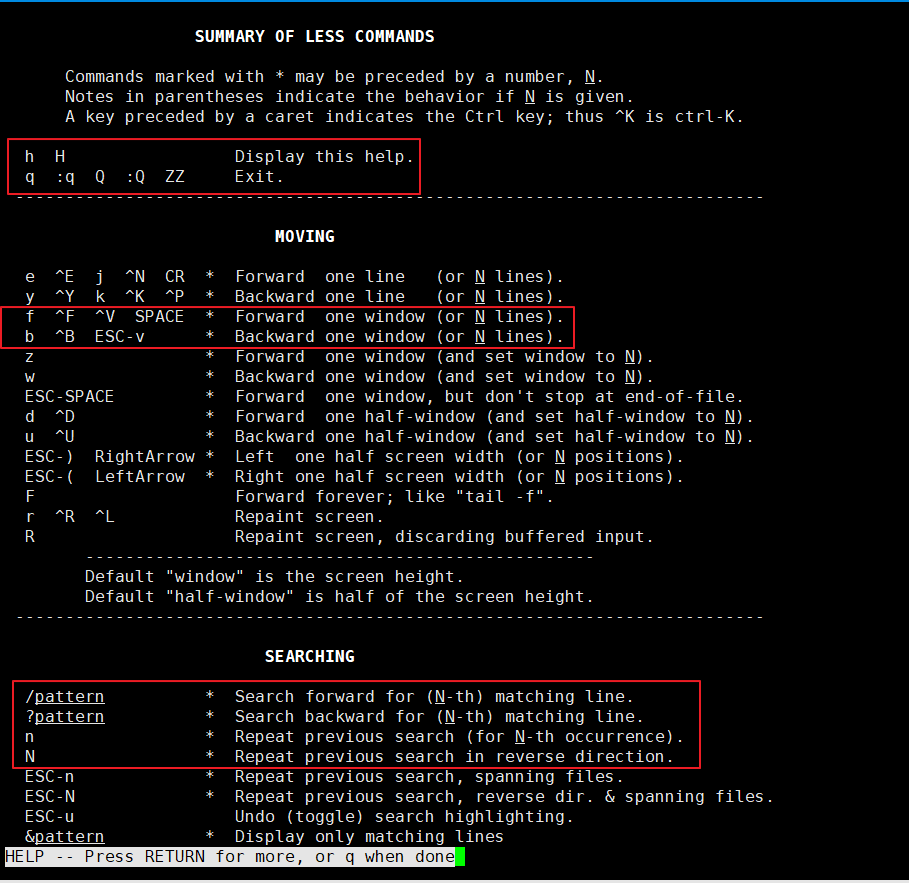
使用vi也可以很方便的查看多行文本,但是当文本文件的大小达到上G(比如开启了debug的日志),还是建议使用less,性能好一点
开多个窗口使用vi打开同一个文件是会报错的,使用less不会
head
head --help
man head
info head
# head --help
Usage: head [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Print the first 10 lines of each FILE to standard output.
With more than one FILE, precede each with a header giving the file name.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-n, --lines=[-]K print the first K lines instead of the first 10;
with the leading '-', print all but the last
K lines of each file
-q, --quiet, --silent never print headers giving file names
-v, --verbose always print headers giving file names
--help display this help and exit
[root@node1 ~]# head /etc/services
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
#
# Network services, Internet style
# IANA services version: last updated 2013-04-10
#
# Note that it is presently the policy of IANA to assign a single well-known
# port number for both TCP and UDP; hence, most entries here have two entries
# even if the protocol doesn't support UDP operations.
# Updated from RFC 1700, ``Assigned Numbers'' (October 1994). Not all ports
[root@node1 ~]# head -n 2 -v /etc/services
==> /etc/services <==
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
tail
# tail --help
Usage: tail [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Print the last 10 lines of each FILE to standard output.
With more than one FILE, precede each with a header giving the file name.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
-f 持续追踪该文件的最后更新内容,多用于查看日志
-F 基本功能和 -f 一致,但是当指定的文件不存在不会报错,会持续追踪,直到该文件出现
可以用在某些文件会被删除自动重建的场景
也多用于docker容器中的测试
-n, --lines=K output the last K lines, instead of the last 10;
or use -n +K to output starting with the Kth
-v, --verbose always output headers giving file names
tail --help
man tail
info tail
[root@node1 ~]# cat -n /etc/services | tail
11167 3gpp-cbsp 48049/tcp # 3GPP Cell Broadcast Service Protocol
11168 isnetserv 48128/tcp # Image Systems Network Services
11169 isnetserv 48128/udp # Image Systems Network Services
11170 blp5 48129/tcp # Bloomberg locator
11171 blp5 48129/udp # Bloomberg locator
11172 com-bardac-dw 48556/tcp # com-bardac-dw
11173 com-bardac-dw 48556/udp # com-bardac-dw
11174 iqobject 48619/tcp # iqobject
11175 iqobject 48619/udp # iqobject
11176 matahari 49000/tcp # Matahari Broker
tailf
功能和 tail -f 基本一致,挺常用的
[root@node1 ~]# tailf --help
Usage:
tailf [option] file
Options:
-n, --lines NUMBER output the last NUMBER lines
-NUMBER same as `-n NUMBER'
-V, --version output version information and exit
-h, --help display this help and exit
wc
# whatis wc
wc (1) - print newline, word, and byte counts for each file
wc --help
只关心,一个文本文件有多少行时常用,比如查看一下系统使用了多少线程
[root@node1 ~]# pstree -a | wc -l
36
[root@node1 ~]# wc -l /etc/services
11176 /etc/services
ping
# whatis ping
ping (8) - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts
ping -h
man ping
info ping
在linux操作系统下,默认是会持续不间断ping的
ping baidu.com
指定ping的次数
# ping -c 2 jd.com
PING jd.com (111.13.149.108) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from jd.com (111.13.149.108): icmp_seq=1 ttl=49 time=12.8 ms
64 bytes from jd.com (111.13.149.108): icmp_seq=2 ttl=49 time=10.3 ms
--- jd.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 10.312/11.598/12.885/1.291 ms
场景:检测某台机器是否在线
[root@node1 tmp]# ping -c 2 -W 3 jd.com
PING jd.com (120.52.148.118) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from jd.com (120.52.148.118): icmp_seq=1 ttl=47 time=7.13 ms
64 bytes from jd.com (120.52.148.118): icmp_seq=2 ttl=47 time=7.05 ms
--- jd.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 7.054/7.093/7.133/0.093 ms
[root@node1 tmp]# echo $?
0
[root@node1 tmp]# ping -c 2 -W 3 192.168.1.188
PING 192.168.1.188 (192.168.1.188) 56(84) bytes of data.
From 192.168.1.112 icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
From 192.168.1.112 icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable
--- 192.168.1.188 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 0 received, +2 errors, 100% packet loss, time 1002ms
pipe 2
[root@node1 tmp]# echo $?
1
这里我们用了两个参数,一个是ping的次数是2次,第2个是每次ping等待的时间是3秒
场景:持续观察到某台机器通信的延时情况
[root@node1 ~]# > ping.txt
[root@node1 ~]# nohup ping baidu.com &>> ping.txt &
[2] 5186
[root@node1 ~]# tail -f ping.txt
nohup: ignoring input
PING baidu.com (39.156.69.79) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from baidu.com (39.156.69.79): icmp_seq=1 ttl=50 time=9.09 ms
64 bytes from baidu.com (39.156.69.79): icmp_seq=2 ttl=50 time=8.79 ms
64 bytes from baidu.com (39.156.69.79): icmp_seq=5 ttl=50 time=7.82 ms
64 bytes from baidu.com (39.156.69.79): icmp_seq=9 ttl=50 time=8.86 ms
64 bytes from baidu.com (39.156.69.79): icmp_seq=10 ttl=50 time=6.93 ms
^C
[root@node1 ~]#
netstat
[root@node1 ~]# netstat -lntup
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:46791 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3167/rpc.statd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:20048 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3212/rpc.mountd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3153/sshd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2049 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:43682 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 3207/mysqld
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::20048 :::* LISTEN 3212/rpc.mountd
tcp6 0 0 :::32977 :::* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 3153/sshd
tcp6 0 0 :::39991 :::* LISTEN 3167/rpc.statd
tcp6 0 0 :::2049 :::* LISTEN -
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:947 0.0.0.0:* 2903/rpcbind
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:20048 0.0.0.0:* 3212/rpc.mountd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2049 0.0.0.0:* -
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* 1/systemd
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:* 3173/chronyd
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:799 0.0.0.0:* 3167/rpc.statd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:56221 0.0.0.0:* -
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:58277 0.0.0.0:* 3167/rpc.statd
udp6 0 0 :::947 :::* 2903/rpcbind
udp6 0 0 :::20048 :::* 3212/rpc.mountd
udp6 0 0 :::2049 :::* -
udp6 0 0 :::36881 :::* -
udp6 0 0 :::111 :::* 1/systemd
udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::* 3173/chronyd
udp6 0 0 :::37489 :::* 3167/rpc.statd
[root@node1 ~]# netstat -lntup | grep 3306
tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 3207/mysqld
ifconfig
[root@node1 ~]# ifconfig
docker0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 172.17.0.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255
ether 02:42:04:8b:f8:a3 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.112 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
inet6 2408:8207:789f:be20:a00:27ff:fee7:284 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0<global>
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fee7:284 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 08:00:27:e7:02:84 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 41756 bytes 3169088 (3.0 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 12638 bytes 4871911 (4.6 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 14 bytes 1372 (1.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 14 bytes 1372 (1.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ip
[root@node1 ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:e7:02:84 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.112/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 2408:8207:789f:be20:a00:27ff:fee7:284/64 scope global mngtmpaddr dynamic
valid_lft 259200sec preferred_lft 172800sec
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fee7:284/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:04:8b:f8:a3 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
find
将/data 目录下的修改时间是 7 天以前,并且大于 100k 的文件 复制到 到/tmp 目录下。
find /data/ -mtime +7 -type f -size +100k | xargs cp -t /tmp/
查找出系统中大于 50k 且小于 100k 的文件, 把 文件中的 的 as4k 替换为 为 oldgirl 。
find / -type f -size +50k -size -100k | xargs sed -i 's#as4k#oldgirl#g'
00 00 * * * /usr/bin/find /data/as4k/log -type f -mtime +20 -name "*.log*" -exec rm -rf {} \; &> /dev/null
找出系统中全部文本文件
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4767396/linux-command-how-to-find-only-text-files
find . -type f -exec grep -Iq . {} \; -print
watch
watch -d uptime
-d 高亮显示变化的部分
w
- 查看负载
- 查看系统一共运行多长时间 (经常用来判断系统是否意味重启)
查看当前登录的用户
[root@10-255-20-218 ~]# w 23:14:19 up 15 days, 13:02, 2 users, load average: 0.01, 0.07, 0.12 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT dc2-user ttyS0 24Mar20 15days 0.16s 0.07s login -- dc2-user root pts/0 221.218.209.221 23:04 3.00s 0.02s 0.00s w
alias
查看系统里的别名 alias
设置别名 alias cp='cp -i'
取消设置别名 unalias cp
永久设置别名 echo "alias cp='cp -i'" >> /etc/profile
取消别名影响的3种方法
\cp /mnt/test.txt /tmp/
/bin/cp /mnt/test.txt /tmp/
unalias cp && cp /mnt/test.txt /tmp/
tac 文本倒序输出
[root@xingyongsheng token]# cat /tmp/tmp.txt
1
2
3
4
[root@xingyongsheng token]# tac /tmp/tmp.txt
4
3
2
1
date
date "+%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M"
date "+%Y_%m_%d %H:%M:%S"
date "+%T"
date "+%F"
sort
ps aux | sort -rnk3 | head
du -sh * | sort -rhk1 | head
awk '{print $1}' nginx.log | sort -h | uniq -c | sort -h | tail -10
uniq
去除重复
uniq /tmp/tmp.txt
fping -a -g 10.39.123.0/24
fping -a -g 10.39.123.0/24 #探测活着的
fping -u -g 10.39.123.0/24 #探测挂了的
fping baidu.com
[root@bx173.sae /usr/home/yongsheng8]# fping baidu.com
baidu.com is alive
fuser
查找某个文件是哪个进程使用的
# fuser -m -v /data0/hadoop/namenode_nfs
USER PID ACCESS COMMAND
/data0/hadoop/namenode_nfs:
root kernel mount /data0/hadoop/namenode_nfs
root 169835 F.... java
# jps
20063 HQuorumPeer
169835 NameNode
45450 Jps